Table of Contents
Instructions:
- Time allowed: 90 minutes
- Total marks: 100 (30 marks for Section A, 70 marks for Section B)
- Answer ALL questions
- Write your answers clearly in the spaces provided
- Show all working for calculations
SECTION A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS [30 marks] #
Choose the best answer for each question. Each question is worth 1 mark.
1. Which statement correctly describes an exothermic reaction?
2. When solid ammonium chloride dissolves in water, the temperature of
the solution decreases. This process is:
3. Which of the following is an example of an exothermic reaction?
4. The enthalpy change (ΔH) for an endothermic reaction is:
5. What is activation energy?
6. In a reaction pathway diagram, the activation energy is shown as:
7. Bond breaking is:
8. Which process releases energy?
9. Look at this reaction pathway diagram:
What is the enthalpy change (ΔH) for this reaction?
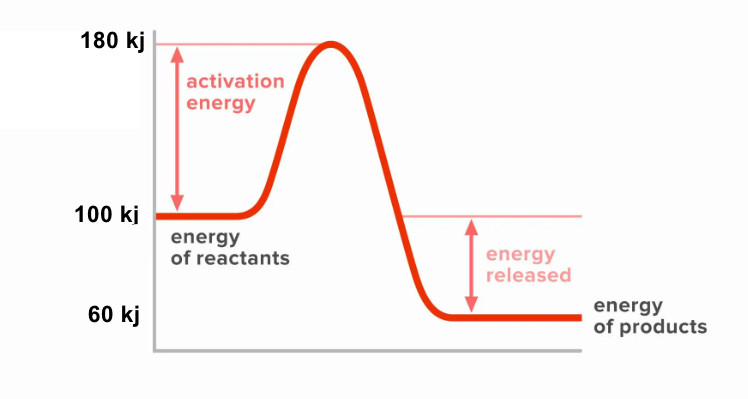
10. Using the same diagram from question 9, what is the activation
energy?
11. In the reaction: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O, how many bonds are broken in
total?
12. A reaction has an enthalpy change of -286 kJ/mol. This means:
13. Which factor does NOT affect the enthalpy change of a reaction?
14. When calculating enthalpy change using bond energies, the formula is:
15. A student touches a test tube where magnesium is reacting with
hydrochloric acid. The test tube feels hot. This indicates:
16. Which statement about catalysts is correct?
17. In the reaction N₂ + 3H₂ → 2NH₃, how many N-H bonds are formed?
18. The bond energy of H-H is 435 kJ/mol. This means:
19. Which reaction pathway diagram represents an endothermic reaction?
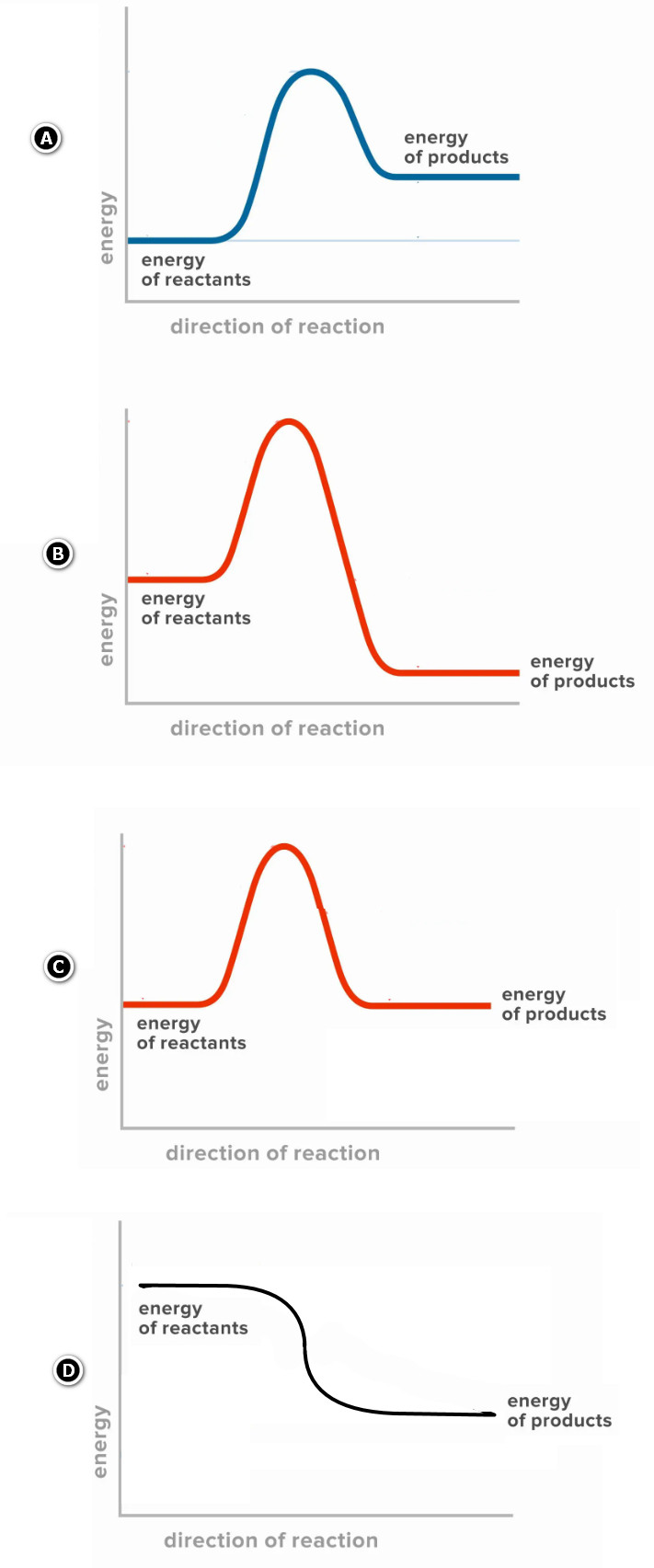
20. During respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen to produce carbon
dioxide and water. This process:
21. A reaction has these bond energies:
What is the enthalpy change?
| Bonds broken: 1000 kJ |
| Bonds formed: 1200 kJ |
22. Why does a match need to be struck before it burns?
23. Which diagram correctly shows the effect of a catalyst?
24. The reaction 2HI → H₂ + I₂ involves breaking 2 H-I bonds. If the
H-I bond energy is 298 kJ/mol, how much energy is needed to break all bonds?
25. Which process is endothermic?
26. In an experiment, citric acid reacts with sodium hydrogencarbonate.
The temperature drops from 20°C to 15°C. What type of reaction is this?
27. The reaction CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O has ΔH = -890 kJ/mol.
This means:
28. Which bond is likely to have the highest bond energy?
29. A reaction profile shows the peak at 150 kJ, reactants at 50 kJ, and
products at 30 kJ. Which statement is correct?
30. Why must all chemical reactions have an activation energy?
SECTION B: WRITTEN RESPONSE QUESTIONS [70 marks] #
Answer all questions in the spaces provided. Show all working for calculations.
1. Define the following terms: [4]
- Exothermic reaction (2 marks)
_____________________
_____________________ - Activation energy (2 marks)
_____________________
_____________________
2. Give two examples of exothermic reactions and two examples of
endothermic reactions that happen in everyday life. [4]
Exothermic:
1. _____________________
2. _____________________
Endothermic:
1. _____________________
2. _____________________
Exothermic:
1. _____________________
2. _____________________
Endothermic:
1. _____________________
2. _____________________
3. A student adds calcium oxide to water in a beaker. The reaction can be
shown as:
CaO + H₂O → Ca(OH)₂
- The student notices the beaker becomes very hot. What type of reaction is this? [1]
_____________________ - What is the sign of ΔH for this reaction? Explain your answer. [2]
_____________________
_____________________
4. Explain why bond breaking is endothermic and bond making is
exothermic. Use the idea of energy in your answer. [4]
_____________________
_____________________
_____________________
_____________________
_____________________
_____________________
_____________________
_____________________
5. The diagram shows a reaction pathway for the decomposition of hydrogen
peroxide:
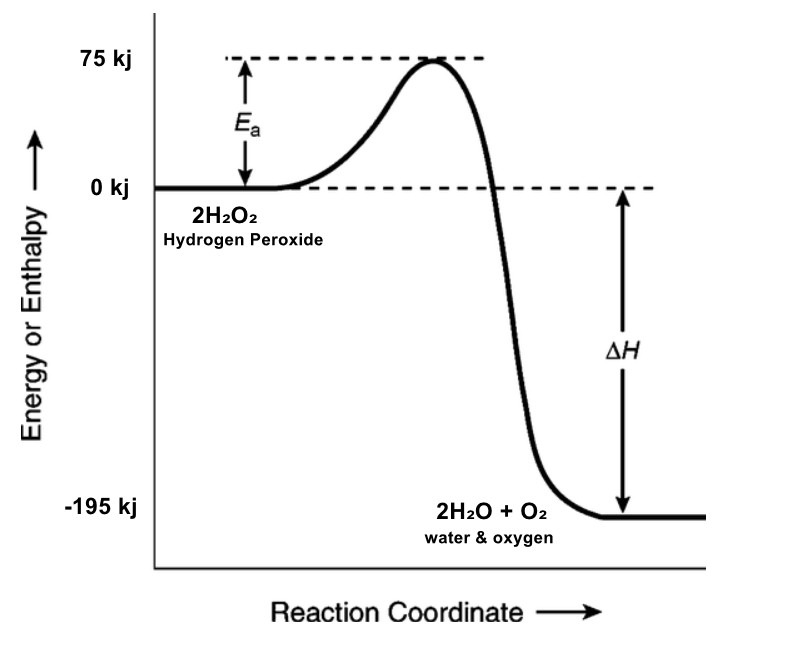
- What is the activation energy for this reaction? [1]
_____________________ - What is the enthalpy change (ΔH) for this reaction? [1]
_____________________ - Is this reaction exothermic or endothermic? Explain how you know. [2]
_____________________
_____________________
6. Photosynthesis is an important endothermic reaction in plants:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
- Where does the energy for this reaction come from? [1]
_____________________ - Explain why this reaction is endothermic in terms of the energy of reactants and products. [2]
_____________________
_____________________ - What would be the sign of ΔH for this reaction? [1]
_____________________
7. Draw and label a complete reaction pathway diagram for an exothermic
reaction where: [4]
- The reactants have an energy of 150 kJ/mol
- The products have an energy of 50 kJ/mol
- The activation energy is 80 kJ/mol
8. Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction: H₂ + Cl₂
→ 2HCl [5]
Use these bond energies:
Show all your working.
Use these bond energies:
| Bond | Bond energy (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|
| H-H | 435 |
| Cl-Cl | 240 |
| H-Cl | 430 |
9. A student investigates the reaction between zinc and copper sulfate
solution:
Zn + CuSO₄ → ZnSO₄ + Cu
The temperature rises from 18°C to 26°C.
- Is this reaction exothermic or endothermic? [1]
_____________________ - Explain your answer to part (a) using the temperature change. [2]
_____________________
_____________________ - Predict the sign of ΔH for this reaction. [1]
_____________________
10. The combustion of ethanol can be represented as:
C₂H₅OH + 3O₂ → 2CO₂ + 3H₂O
- State whether this reaction is exothermic or endothermic. [1]
_____________________ - Explain why all combustion reactions have the same type of energy change. [2]
_____________________
_____________________ - Why does ethanol need a spark or flame to start burning? [2]
_____________________
_____________________
11. Calculate the enthalpy change for: CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O [6]
Bond energies (kJ/mol):
Show all steps of your calculation.
Bond energies (kJ/mol):
| Bond | Energy | Bond | Energy |
|---|---|---|---|
| C-H | 410 | C=O | 740 |
| O=O | 498 | O-H | 460 |
12. A reaction has the following energy values:
- Energy needed to break bonds = 850 kJ/mol
- Energy released when bonds form = 920 kJ/mol
- Calculate the enthalpy change (ΔH) for this reaction. [2]
_____________________ - Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? [1]
_____________________ - Sketch a reaction pathway diagram for this reaction. [3]
13. Explain the difference between enthalpy change (ΔH) and
activation energy (Ea). Include what each one measures in a chemical reaction. [4]
_____________________
_____________________
_____________________
_____________________
_____________________
_____________________
_____________________
_____________________




