The elements of weather are the different components that make up the conditions in the atmosphere in a particular place.
These are the main elements of weather
- Sunshine
- Pressure
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Precipitation
- Wind direction
- Wind speed
Each of these elements plays an important role in shaping the weather conditions experienced in a region.
| Weather Element | Instruments Used | Measured In (units) |
| Sunshine | Campbell–Stokes Sunshine Recorder | Hours Per Day |
| Pressure | 1) Mercury Barometer 2) Aneroid Barometer | Millibars (mb) |
| Temperature | Thermometer | Degrees Celsius (°C) |
| Humidity | Hygrometer | Percentage (%) |
| Precipitation (rain fall) | Rain Gauge | Millimeters (mm) |
| Wind Direction | Wind Vane | Direction (North West, South, etc) |
| Wind Speed | Anemometer | Kilometers per hour (km/h) |
Sunshine #
Sunshine is the light and warmth we get from the sun. It is needed by both humans and plants for life to exists.
Sunshine is measured using a Campbell–Stokes Sunshine Recorder
Campbell–Stokes Sunshine Recorder
A Campbell–Stokes Sunshine Recorder is a simple device used to measure how much sunshine is in a particular day. It is made of a glass sphere called a “burning glass” that is mounted in a metal frame.
How it Works
- The recorder is placed in an open area, on a flat surface facing the sun.
- When sunlight hits the glass sphere, it focuses the sunlight on a strip of special paper
- As the day continues, the sun moves and burns a line on the special paper
- The paper has a ruler that is the number of hours in a day
- The length of the burnt line tells us how many hours of sunshine we had

Pressure #
In weather, pressure is how much the air around us, (the atmosphere) pushes down on the Earth.
- It is like the weight of the air above us.
- When pressure is high, it usually means sunny weather.
- When it’s low, we might expect rain or storms.
- We measure pressure with tools called barometers.
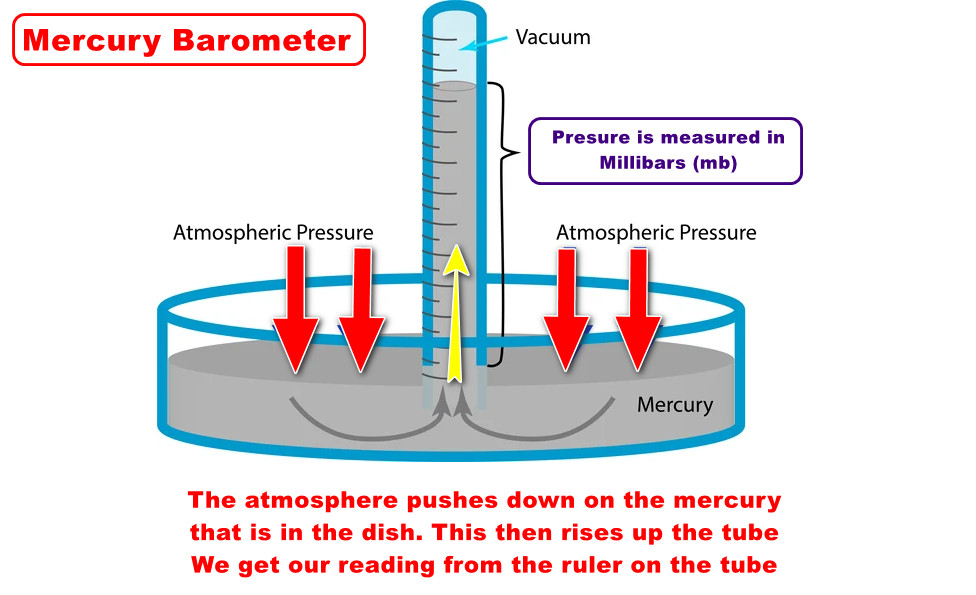
(1) Measuring Pressure – Mercury Barometer #
- There’s a tube filled with mercury, a shiny liquid metal.
- The tube is turned upside down and placed in a dish of more mercury.
- The mercury in the tube pushes down, creating a vacuum, or empty space, at the top.
- When pressure is high, the mercury rises in the tube.
- When it’s low, the mercury drops.
- We measure the height of the mercury to know the air pressure
(2) Measuring Pressure – Aneroid Barometer #
Another instrument used to measure atmosphere is called an aneroid barometer (the word aneroid mean ‘without liquid’)
An aneroid barometer is a device used to measure atmospheric pressure without using liquid mercury. Instead of mercury, it has a small, flexible metal box inside that contracts or expands as air pressure changes. This movement is connected to a pointer on a dial, which shows the pressure readings

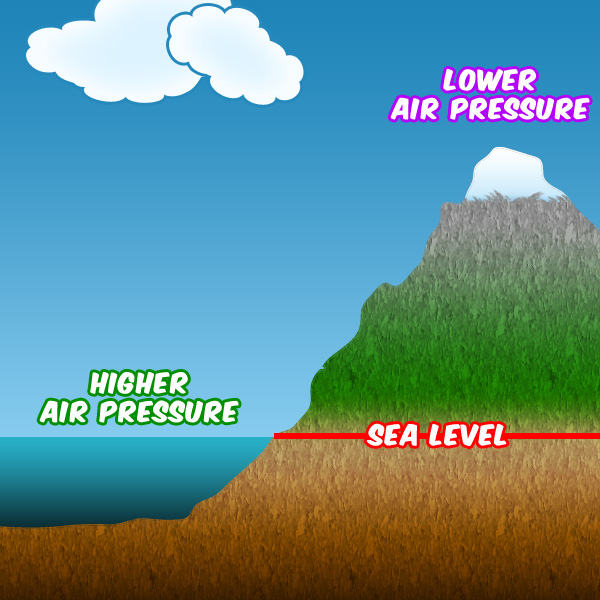
Changes in pressure the higher you go #
The pressure of the atmosphere on the earth gets less (decreases) the higher up you go. This means pressure is low when you are on top of a mountain and it is high when you are on the ground level.
- Air pressure is low on the top of a mountain
- Air pressure is high at the ground level (also called sea level)
This is because the lower you are, the more air that is on top of you. It is like a person who is under 100 blankets. They will feel more weight of the blankets that a person on the top who only has a few blankets on top of them
Temperature #
Temperature refers to how hot or cold the air is. It’s measured in degrees Celsius (°C).
Measuring Temperature – Six’s Thermometer
To measure temperature, we use a tool called a thermometer. There are different types, but one common type is the Six’s thermometer (it is also called the minimum-maximum thermometer).
It was invented by a man named James Six. This is why it is called the Six’s thermometer
This type of thermometer records the lowest and highest temperatures reached in a given day or period.

Humidity #
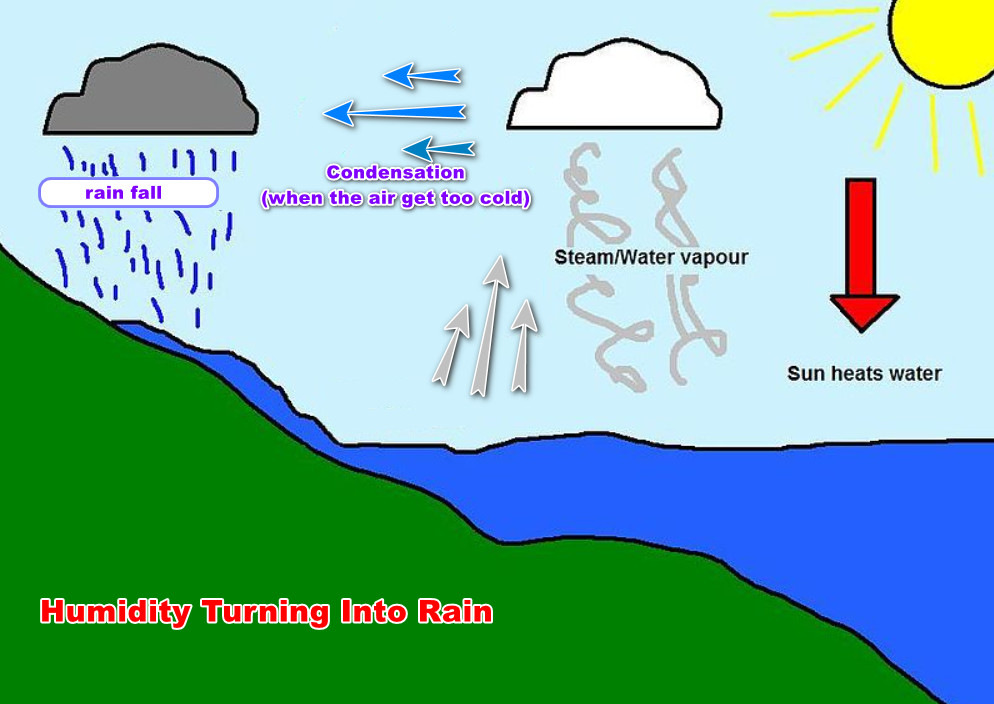
Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. Water vapor is water in gas form and it is invisible.
When it is hot, water evaporates from places like the ocean, rivers, ponds. It them enters into the atmosphere.
When air cools down, it is unable to hold anymore water vapor. When the air can not hold anymore water vapor, it said to have become saturated. This point is called the Dew Point.
When cold air reaches its dew point, we start to see the see the moisture in the form of mist, clouds or fog.

If the air keeps cooling down even further, it will start to turn into liquid in a process called Condensation (condensation is when water gas turns into liquid) We then get rain.
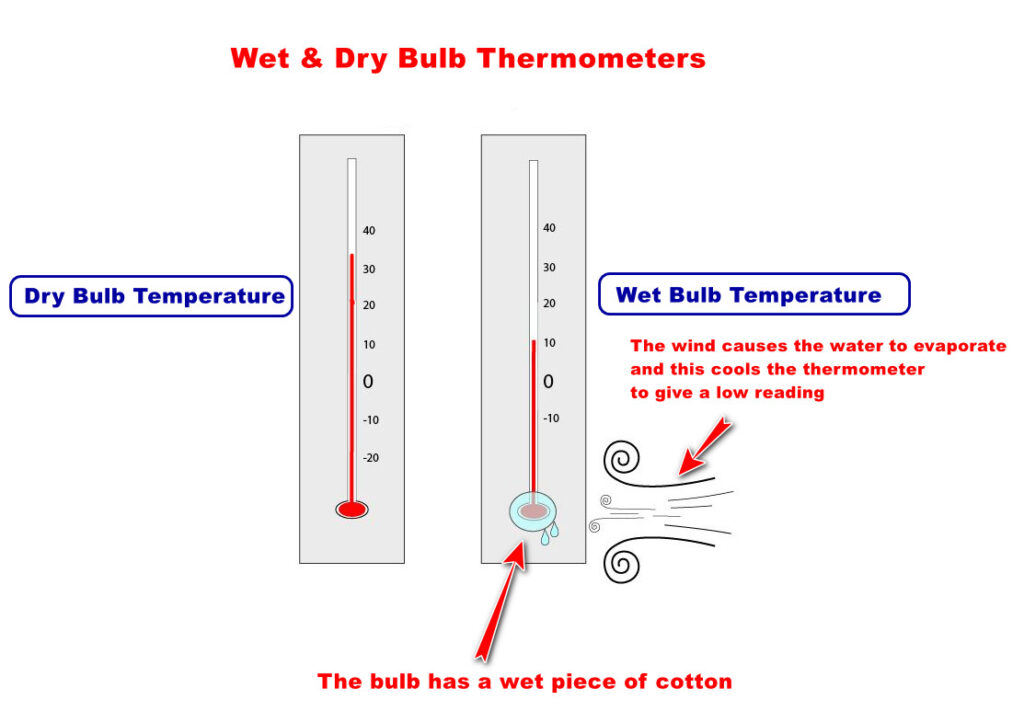
Measuring Humidity – Wet & Dry Bulb Thermometer
A wet and dry bulb thermometer is a device used to measure humidity.
- Dry-bulb temperature (the temperature of the air)
- Wet-bulb temperature (the lowest temperature that can be reached by evaporating water into the air).
Dry-Bulb Thermometer:
This thermometer measures the temperature of the air. It’s called “dry” because the bulb of the thermometer is left dry, meaning it’s not affected by moisture.
Wet Bulb Thermometer
This thermometer has its bulb covered with a piece of fabric (called a wick) that is kept moist using water. As the water evaporates from the fabric, it causes cooling. The temperature displayed by this thermometer represents the lowest temperature that can be reached by cooling on that day.
Precipitation #
Precipitation is any form of water, (in liquid or solid form), that falls from the atmosphere and reaches the Earth’s surface. This includes rain, snow, and hail.
Precipitation is an important part of the Earth’s water cycle and it is an important weather element.
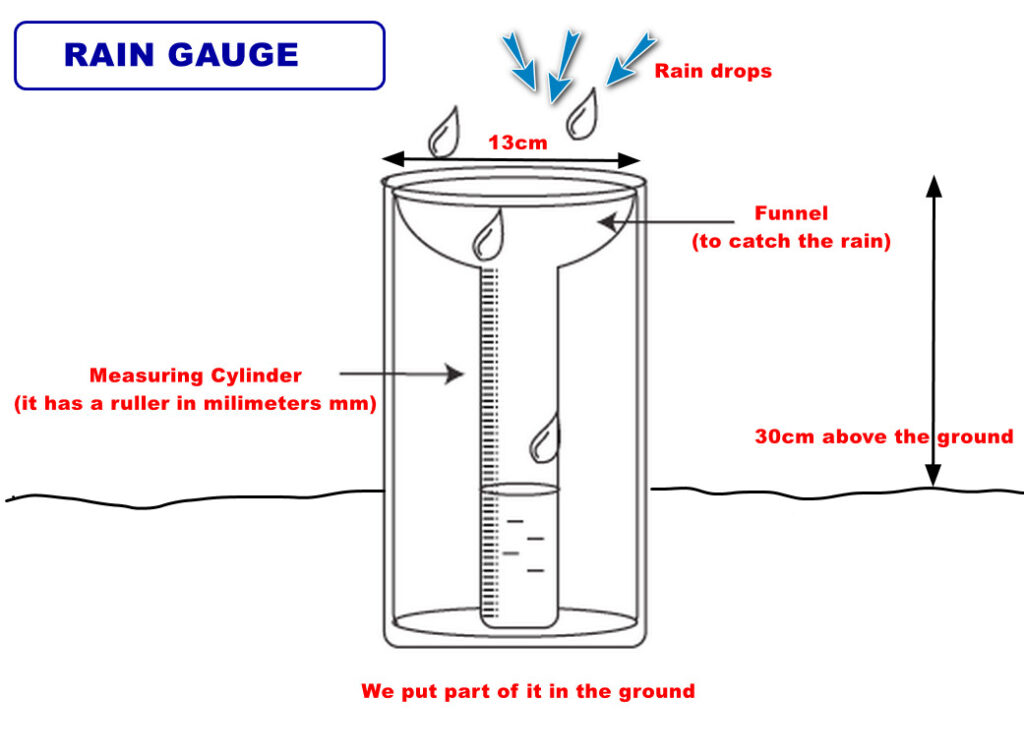
Rain Gauge #
A rain gauge is the most common instrument that is used to measure rain. It is made up of a cylindrical container with a funnel at the top to collect precipitation and a ruler scale to measure the amount of water collected.
The collected water is measured in millimeters (mm).