Table of Contents
How to use this answer sheet:
- Check your answers against the correct answers shown in green
- Read the explanations to understand why each answer is correct
- Review the revision notes for important concepts
SECTION A: MULTIPLE CHOICE ANSWERS [15 marks] #
1. Which of the following is the main function of carbohydrates in the body?
Answer: B – Providing energy for body activities
Why this answer is correct:
Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy. They are broken down into glucose, which cells use for energy in activities like movement, breathing, and thinking. Building cells is the job of proteins, protecting organs is done by lipids, and fighting diseases is done by proteins (antibodies).
Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy. They are broken down into glucose, which cells use for energy in activities like movement, breathing, and thinking. Building cells is the job of proteins, protecting organs is done by lipids, and fighting diseases is done by proteins (antibodies).
2. A person who does not eat enough vitamin C may develop a disease called:
Answer: C – Scurvy
Why this answer is correct:
Scurvy is caused by a lack of vitamin C. Symptoms include bleeding gums, loose teeth, and poor wound healing. Rickets is caused by vitamin D or calcium deficiency. Anaemia is caused by iron deficiency. Diabetes is not a deficiency disease.
Scurvy is caused by a lack of vitamin C. Symptoms include bleeding gums, loose teeth, and poor wound healing. Rickets is caused by vitamin D or calcium deficiency. Anaemia is caused by iron deficiency. Diabetes is not a deficiency disease.
3. Which nutrient is needed to make haemoglobin in red blood cells?
Answer: B – Iron
Why this answer is correct:
Iron is needed to make haemoglobin, which is the red pigment in red blood cells that carries oxygen around the body. Without enough iron, the body cannot make enough red blood cells, leading to anaemia.
Iron is needed to make haemoglobin, which is the red pigment in red blood cells that carries oxygen around the body. Without enough iron, the body cannot make enough red blood cells, leading to anaemia.
4. Lipids (fats and oils) are stored in the body. Which of the following is NOT a function of this stored fat?
Answer: C – Making enzymes to control chemical reactions
Why this answer is correct:
Enzymes are made from proteins, not lipids. Stored fat does provide energy reserves, insulation (keeping you warm), and protection for organs. Lipids have many functions, but making enzymes is not one of them.
Enzymes are made from proteins, not lipids. Stored fat does provide energy reserves, insulation (keeping you warm), and protection for organs. Lipids have many functions, but making enzymes is not one of them.
5. Which food group contains the most protein?
Answer: C – Meat, fish, and eggs
Why this answer is correct:
Meat, fish, and eggs are all animal products that are rich in protein. Rice, bread, and pasta contain mainly carbohydrates. Butter and oils are lipids. Citrus fruits contain mainly vitamin C and carbohydrates.
Meat, fish, and eggs are all animal products that are rich in protein. Rice, bread, and pasta contain mainly carbohydrates. Butter and oils are lipids. Citrus fruits contain mainly vitamin C and carbohydrates.
6. A child has soft, bent leg bones and does not grow properly. The child is most likely suffering from:
Answer: B – Rickets
Why this answer is correct:
Rickets causes soft, bent bones (especially leg bones) and poor growth in children. It is caused by a deficiency of vitamin D or calcium. Scurvy affects gums and teeth. Anaemia causes tiredness and breathlessness. Obesity is not a deficiency disease.
Rickets causes soft, bent bones (especially leg bones) and poor growth in children. It is caused by a deficiency of vitamin D or calcium. Scurvy affects gums and teeth. Anaemia causes tiredness and breathlessness. Obesity is not a deficiency disease.
7. Which statement about fibre is correct?
Answer: B – Fibre helps food move through the digestive system
Why this answer is correct:
Fibre cannot be digested by the human body, but it adds bulk to food and helps it move through the intestines. This prevents constipation and keeps the digestive system healthy. Fibre does not provide energy, is not stored, and is not used to build cells.
Fibre cannot be digested by the human body, but it adds bulk to food and helps it move through the intestines. This prevents constipation and keeps the digestive system healthy. Fibre does not provide energy, is not stored, and is not used to build cells.
8. A person feels tired all the time, gets breathless easily, and has pale skin. Which nutrient deficiency is the most likely cause?
Answer: D – Iron deficiency
Why this answer is correct:
These are the symptoms of anaemia, which is caused by iron deficiency. Without enough iron, the body cannot make enough haemoglobin to carry oxygen in the blood. This causes tiredness, breathlessness, and pale skin.
These are the symptoms of anaemia, which is caused by iron deficiency. Without enough iron, the body cannot make enough haemoglobin to carry oxygen in the blood. This causes tiredness, breathlessness, and pale skin.
9. Which of these foods is the best source of vitamin D?
Answer: B – Oily fish and eggs
Why this answer is correct:
Oily fish (like salmon and mackerel) and eggs are good sources of vitamin D. Oranges and lemons contain vitamin C. Bread and rice contain carbohydrates. Carrots and spinach contain other vitamins and minerals but not much vitamin D.
Oily fish (like salmon and mackerel) and eggs are good sources of vitamin D. Oranges and lemons contain vitamin C. Bread and rice contain carbohydrates. Carrots and spinach contain other vitamins and minerals but not much vitamin D.
10. Water is essential for the body. Approximately what percentage of the human body is made up of water?
Answer: C – About 70%
Why this answer is correct:
The human body is made up of about 70% water. Water is needed for all chemical reactions in the body, for transport of substances, for temperature control, and as the main component of blood and cells.
The human body is made up of about 70% water. Water is needed for all chemical reactions in the body, for transport of substances, for temperature control, and as the main component of blood and cells.
11. Which nutrient provides more than twice as much energy per gram compared to carbohydrates?
Answer: C – Lipids
Why this answer is correct:
Lipids (fats and oils) provide more than twice as much energy per gram compared to carbohydrates or proteins. This is why the body stores excess energy as fat – it is the most efficient way to store energy.
Lipids (fats and oils) provide more than twice as much energy per gram compared to carbohydrates or proteins. This is why the body stores excess energy as fat – it is the most efficient way to store energy.
12. A person with scurvy might experience:
Answer: B – Bleeding gums and loose teeth
Why this answer is correct:
Scurvy is caused by vitamin C deficiency. Symptoms include bleeding gums, loose teeth, and poor wound healing. Vitamin C is needed to make collagen, which holds cells together. Soft bones are a symptom of rickets. Tiredness is a symptom of anaemia.
Scurvy is caused by vitamin C deficiency. Symptoms include bleeding gums, loose teeth, and poor wound healing. Vitamin C is needed to make collagen, which holds cells together. Soft bones are a symptom of rickets. Tiredness is a symptom of anaemia.
13. Which statement about proteins is correct?
Answer: B – Proteins are made up of smaller units called amino acids
Why this answer is correct:
Proteins are large molecules made up of chains of amino acids joined together. Carbohydrates are the main energy source, not proteins. Proteins can be found in plant foods like beans and nuts. Lipids (not proteins) are stored under the skin for insulation.
Proteins are large molecules made up of chains of amino acids joined together. Carbohydrates are the main energy source, not proteins. Proteins can be found in plant foods like beans and nuts. Lipids (not proteins) are stored under the skin for insulation.
14. An athlete needs more carbohydrates than a person who works in an office. This is mainly because the athlete:
Answer: C – Uses more energy during physical activity
Why this answer is correct:
Athletes do lots of physical activity, which uses a lot of energy. Carbohydrates are the main source of energy, so athletes need more carbohydrates than less active people. While athletes also need protein and water, the question specifically asks about carbohydrates.
Athletes do lots of physical activity, which uses a lot of energy. Carbohydrates are the main source of energy, so athletes need more carbohydrates than less active people. While athletes also need protein and water, the question specifically asks about carbohydrates.
15. Which combination of foods would provide a good source of calcium?
Answer: B – Milk, cheese, and yogurt
Why this answer is correct:
Dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt) are excellent sources of calcium. Calcium is needed for strong bones and teeth. Bread, pasta, and rice provide carbohydrates. Chicken, fish, and eggs provide protein. Butter, oil, and nuts provide lipids.
Dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt) are excellent sources of calcium. Calcium is needed for strong bones and teeth. Bread, pasta, and rice provide carbohydrates. Chicken, fish, and eggs provide protein. Butter, oil, and nuts provide lipids.
SECTION B: WRITTEN RESPONSE ANSWERS [35 marks] #
1. The table below shows the seven components of a healthy diet.
Complete the table by writing one main function for each dietary component.
| Dietary Component | One Main Function |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | _______________________________ |
| Lipids | _______________________________ |
| Proteins | _______________________________ |
| Vitamin C | _______________________________ |
| Calcium | _______________________________ |
| Fibre | _______________________________ |
| Water | _______________________________ |
Complete the table by writing one main function for each dietary component.
| Dietary Component | One Main Function |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | Provide energy for body activities / Main source of energy |
| Lipids | Provide energy / Insulation / Protection of organs / Energy storage |
| Proteins | Growth and repair of cells and tissues / Making enzymes / Making antibodies |
| Vitamin C | Needed to make collagen / Helps wounds heal / Prevents scurvy |
| Calcium | Strong bones and teeth / Prevents rickets / Needed for blood clotting |
| Fibre | Helps food move through the digestive system / Prevents constipation |
| Water | Needed for all chemical reactions / Main component of blood / Temperature control / Transport |
Important: For each nutrient, any of the correct functions listed would be acceptable. You only need to give ONE main function for each.
2. Vitamin D is an important nutrient for the body.
- Give two food sources that contain vitamin D.
- Apart from food, state one other way the body can get vitamin D.
- Explain why vitamin D is important for the body.
a) Two food sources of vitamin D:
- Oily fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Eggs
- Milk / Dairy products
- Butter / Margarine (fortified)
Any two of the above foods are correct.
b) Other way to get vitamin D:
- Sunlight on the skin / UV light
- The body makes vitamin D when skin is exposed to sunlight
- Needed for strong bones and teeth
- Helps the body absorb calcium from food
- Prevents rickets
Why this is important: Vitamin D helps calcium be absorbed in the intestines. Without vitamin D, even if you eat calcium, your body cannot use it properly. This is why vitamin D deficiency causes rickets (soft bones).
3. The diagram below shows a plate of food that represents a balanced meal.

- Explain what is meant by the term “balanced diet”.
- Give two reasons why a teenage girl might need a different diet compared to an elderly man.
a) Balanced diet means:
- A diet that contains all seven dietary components (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, vitamins, minerals, fibre, water) in the correct amounts/proportions
- Eating a variety of different foods to get all the nutrients the body needs
- Not eating too much or too little of any nutrient
Key point: A balanced diet is different for different people – it depends on age, activity level, sex, and health. The correct proportions vary from person to person.
b) Two reasons why a teenage girl needs a different diet:
- The teenage girl is still growing, so needs more protein for growth and more calcium for strong bones
- The elderly man is less active, so needs less energy (fewer carbohydrates and lipids)
- The teenage girl needs more iron because she loses blood during menstruation
- The teenage girl needs more energy because she is more active
Any two sensible comparisons are acceptable. The key is to identify that teenagers are growing and usually more active than elderly people.
4. Rickets is a disease that affects bone development in children.
- State two symptoms of rickets.
- Name two nutrients that can cause rickets if they are not eaten in enough amounts.
- Suggest why children who spend most of their time indoors might be at greater risk of developing rickets.
a) Two symptoms of rickets:
- Soft bones
- Bent legs / Bowed legs
- Poor growth / Short height
- Weak bones that break easily
Any two of these symptoms are correct.
b) Two nutrients that can cause rickets:
- Vitamin D
- Calcium
Important: Rickets can be caused by EITHER vitamin D deficiency OR calcium deficiency (or both). These two nutrients work together to build strong bones.
c) Why children who stay indoors are at greater risk:
- They do not get enough sunlight on their skin
- The body needs sunlight/UV light to make vitamin D in the skin
- Without sunlight, they cannot make enough vitamin D, which leads to rickets
This is why rickets used to be common in children who worked in factories during the Industrial Revolution – they spent all day indoors and never got sunlight.
5. The table below shows information about four people with different lifestyles.
| Person | Description |
|---|---|
| Person A | 16-year-old male athlete who trains every day |
| Person B | 30-year-old pregnant woman |
| Person C | 8-year-old child |
| Person D | 70-year-old person who does very little physical activity |
- Which person needs the most energy from carbohydrates? Explain your answer.
- Which person needs extra iron in their diet? Explain why.
- Explain why Person C needs plenty of protein and calcium in their diet.
a) Person who needs most energy from carbohydrates:
- Person A (the 16-year-old athlete)
- He trains every day, so uses a lot of energy during physical activity
- He is also still growing, which needs energy
- Carbohydrates are the main source of energy for muscles during exercise
- Person B (the pregnant woman)
- She needs to make extra blood for the baby
- Iron is needed to make haemoglobin in red blood cells
- The baby is also making its own blood and needs iron
Pregnant women often take iron supplements because it is difficult to get enough iron from food alone.
c) Why Person C needs protein and calcium:
- Person C is an 8-year-old child who is still growing
- Protein is needed for growth – to build new cells and tissues
- Calcium is needed to build strong bones and teeth
- Children’s bones are still developing, so they need plenty of calcium
6. A sailor on a long sea voyage many years ago ate only dried meat and ship’s biscuits. After several weeks, his gums started bleeding and his teeth became loose.
- Name the deficiency disease the sailor is suffering from.
- Which nutrient was missing from his diet?
- Give two examples of foods the sailor should eat to prevent this disease.
a) Deficiency disease:
- Scurvy
- Vitamin C
- Oranges / Lemons / Citrus fruits
- Fresh vegetables (tomatoes, peppers, leafy greens)
- Fresh fruits (strawberries, kiwi, pineapple)
- Potatoes
Historical fact: Scurvy was common among sailors on long voyages because they had no fresh fruit or vegetables. British sailors were called “limeys” because they ate limes to prevent scurvy. Vitamin C cannot be stored in the body, so you need to eat it regularly.
7. The diagram shows the structure of a protein molecule made up of amino acids.
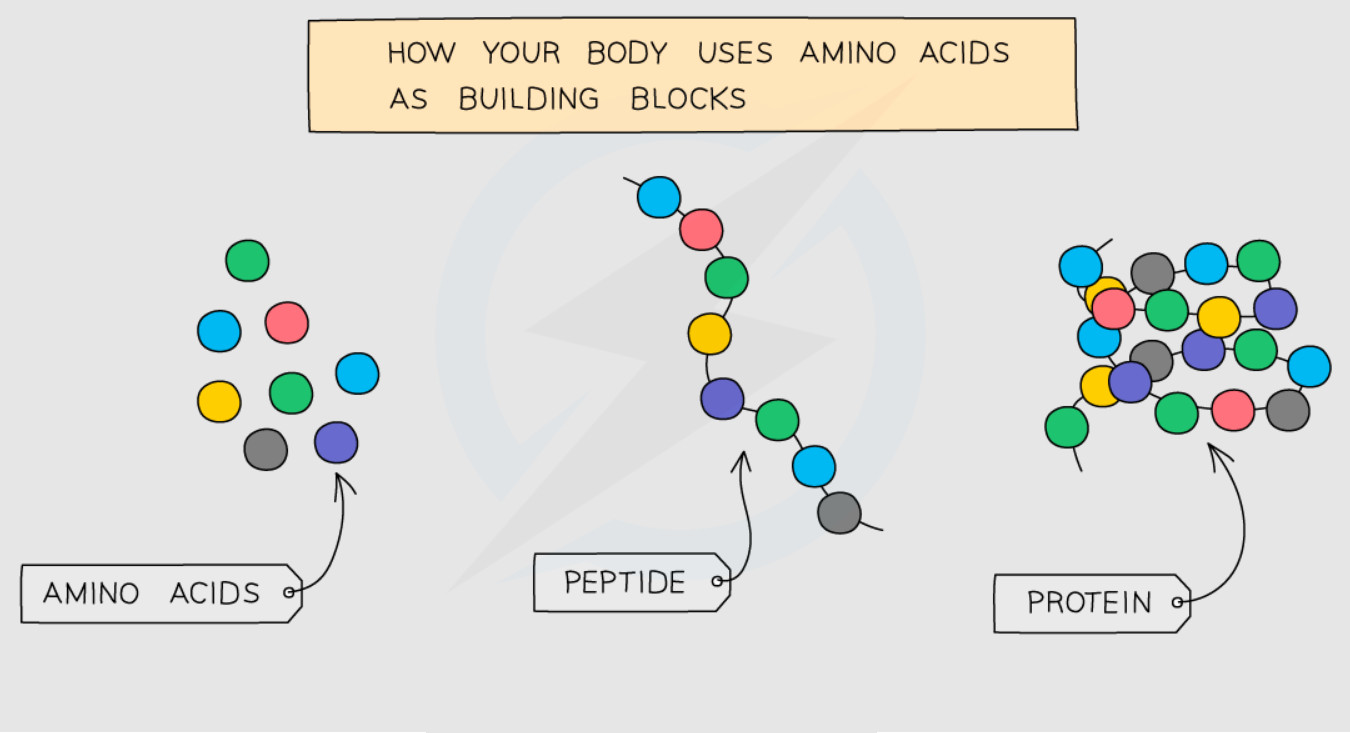
- State what amino acids are joined together to make.
- Give two functions of proteins in the body.
- Explain why vegetarians need to eat a variety of different plant proteins.
a) Amino acids join together to make:
- Proteins
- Protein molecules
- Growth – building new cells and tissues
- Repair – fixing damaged tissues and healing wounds
- Making enzymes to control chemical reactions
- Making antibodies to fight disease
- Making some hormones
- Building hair, nails, and skin
Any two of these functions are correct.
c) Why vegetarians need variety of plant proteins:
- Plant proteins are “incomplete” – they do not contain all the amino acids the body needs
- Different plant foods contain different amino acids
- By eating a variety of plant proteins (beans, nuts, lentils, etc.), vegetarians can get all the amino acids they need
- Animal proteins are “complete” and contain all amino acids, but plant proteins must be combined
Example: Eating rice and beans together provides all the amino acids needed because they complement each other.
8. A person feels tired all the time and gets out of breath easily when climbing stairs. A blood test shows that they have a low number of red blood cells.
- Name the deficiency disease this person has.
- Which mineral is needed to make red blood cells?
- Give two foods rich in this mineral that the person should eat.
a) Deficiency disease:
- Anaemia
- Iron
- Red meat / Beef / Liver
- Dark green leafy vegetables (spinach, kale)
- Beans / Lentils
- Eggs
- Dried fruits (raisins, apricots)
- Fortified breakfast cereals
Why these symptoms occur: Iron is needed to make haemoglobin in red blood cells. Haemoglobin carries oxygen around the body. Without enough red blood cells, not enough oxygen reaches the muscles and organs, causing tiredness and breathlessness.
9. A student is investigating the importance of fibre in the diet.
- Explain why fibre is important for keeping the digestive system healthy.
- Give two examples of foods that contain a lot of fibre.
a) Why fibre is important:
- Fibre adds bulk to food and helps it move through the intestines
- Prevents constipation by keeping food moving
- Helps prevent digestive problems
- Cannot be digested, so it pushes other food through the digestive system
How it works: Fibre is like a brush that sweeps through the intestines. It absorbs water and makes the contents of the intestines soft and bulky, which makes them easier to push along.
b) Two foods rich in fibre:
- Wholegrain bread / Brown bread
- Wholegrain cereals / Bran / Oats
- Brown rice / Whole wheat pasta
- Vegetables (especially with skin on)
- Fruits (especially with skin on)
- Beans / Lentils / Peas
- Nuts and seeds
Wholegrain foods are much better sources of fibre than white/refined foods.
10. The table shows the nutrient content of two different meals.
| Meal | Carbohydrates (g) | Lipids (g) | Proteins (g) | Vitamin C (mg) | Fibre (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meal 1: Burger and chips | 65 | 35 | 20 | 5 | 3 |
| Meal 2: Grilled fish with brown rice and vegetables | 55 | 12 | 30 | 45 | 8 |
- Which meal contains more lipids?
- Explain why Meal 2 is healthier than Meal 1. Give two reasons.
- A teenager eats Meal 1 every day for lunch. Explain what health problems might develop if they continue eating this way.
a) Meal with more lipids:
- Meal 1 (Burger and chips) – contains 35g of lipids
- Meal 2 has much more vitamin C (45mg vs 5mg), which is needed to prevent scurvy and help wounds heal
- Meal 2 has more fibre (8g vs 3g), which helps the digestive system work properly and prevents constipation
- Meal 2 has more protein (30g vs 20g), which is needed for growth and repair
- Meal 2 has less lipids/fat (12g vs 35g), so less risk of obesity and heart disease
- Meal 2 is more balanced with a better variety of nutrients
Any two sensible comparisons are acceptable. The key point is that Meal 2 has more vitamins, fibre, and protein, but less fat.
c) Health problems from eating Meal 1 every day:
- Obesity – too much lipids/fat and energy leads to weight gain
- Heart disease – too much fat can block blood vessels
- Constipation – not enough fibre
- Scurvy – not enough vitamin C
- Type 2 diabetes – linked to obesity
- Poor health from lack of vitamins and minerals
Important concept: Eating the occasional burger and chips is fine, but eating it every day means the diet is not balanced. The teenager would be getting too much of some nutrients (lipids) and not enough of others (vitamins, fibre).
End of Answers
Review any questions you got wrong and make sure you understand why the correct answer is right.




