Chemical bonding explains how atoms join together to form compounds. The two main types of bonding you need to understand for IGCSE are ionic bonding and covalent bonding. Each type creates different structures with distinct properties.
1. Ionic Bonding #
Ionic bonding occurs between a metal and a non-metal. It involves the complete transfer of electrons.
How Ionic Bonding Works #
- Electron Transfer: Metal atoms lose electrons to form positive ions (cations)
- Electron Acceptance: Non-metal atoms gain electrons to form negative ions (anions)
- Attraction: Oppositely charged ions attract each other with strong electrostatic forces
- Structure: Forms giant ionic lattice structures
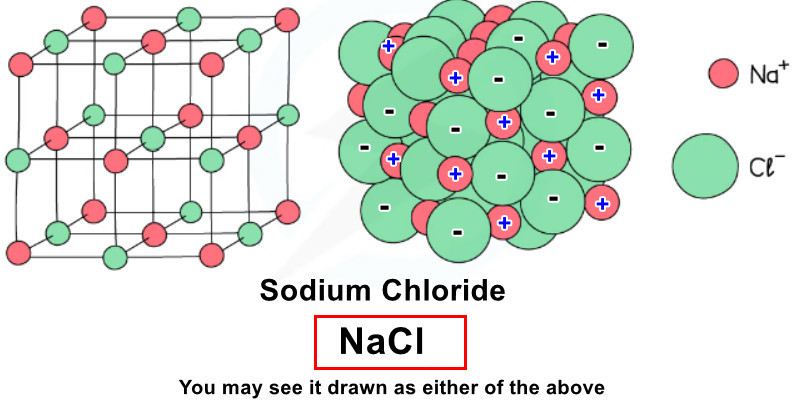
Example: Sodium Chloride (NaCl) #
Sodium (Na) loses 1 electron to form Na+ ion
Chlorine (Cl) gains 1 electron to form Cl– ion
Na+ and Cl– ions are arranged in a giant lattice structure
2. Covalent Bonding #
Covalent bonding occurs between non-metal atoms. It involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
How Covalent Bonding Works #
- Electron Sharing: Atoms share pairs of electrons
- Stability: Sharing helps atoms achieve stable electron configurations
- Bond Strength: Depends on the number of shared electron pairs
Examples: #
Water (H2O): Each hydrogen atom shares an electron pair with oxygen
Oxygen (O2): Two oxygen atoms share two pairs of electrons (double bond)
3. Types of Structures #
Different types of bonding create different structures with unique properties.
Giant Ionic Structures #
- Contains ions arranged in a regular pattern
- Very strong forces between ions (positive and negative charged
- Examples: NaCl, KF, MgO
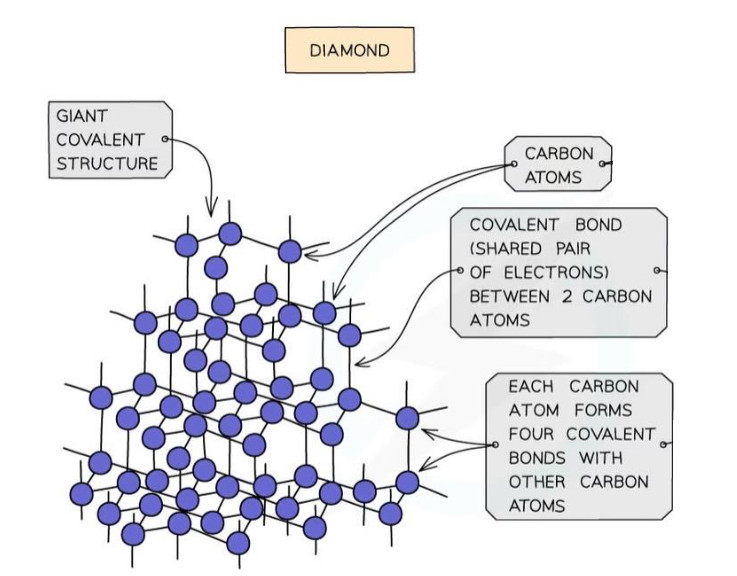
Giant Covalent Structures #
- Contains atoms joined by covalent bonds in a continuous network
- Very strong bonds throughout structure
- Examples: Diamond, Graphite, Silicon dioxide
Simple Molecular Structures #
- Contains small molecules
- Strong bonds within molecules, weak forces between molecules
- Examples: H2O, O2, CO2
4. Comparing Properties #
The table below tell us the various properties and differences between substsances made from ionic, covelant or simple bonds.
| Property | Ionic Substance | Covalent Substance | Simple Molecular |
|---|---|---|---|
| State at room temperature | Solid | Solid | Usually gas or liquid |
| Boiling points | High | Very high | Low |
| Conduct electricity when solid | No | Varies (graphite yes, diamond no) | No |
| Conduct electricity when melted/dissolvedd | Yes | No | No |
| Soluble in water | Yes | No | Sometimes |
| Strength | Hard | Very hard | Soft |




