-
a) Completing the table:
For each particle, charge = number of protons – number of electrons
Particle Protons Electrons Neutrons Charge A 20 18 18 +2 B 17 17 20 0 C 9 9 10 0 D 17 17 18 0 E 13 10 14 +3 F 16 18 19 -2 b) Nucleon number of E
= number of protons + number of neutrons
= 13 + 14 = 27
c) Particles B and D are isotopes because they:
- Have same number of protons (17)
- Have different number of neutrons (20 and 18)
d) F has 16 protons, which corresponds to Sulfur (S) in the periodic table
-
Completing the table:
Particle Protons Electrons Electronic configuration Charge A 20 18 2,8,8 +2 B 9 10 2,8 -1 C 10 10 2,8 0 D 8 10 2,8 -2 -
Identifying structures:
- a) B – atoms with full outer shell of electrons = Ne (neon)
- b) E – giant covalent structure
- c) D – particles formed by loss and gain of electrons (ionic compound KF)
- d) A – conducts electricity when solid (metallic structure)
- e) D – conducts electricity when molten/dissolved
- f) C – lowest melting point (simple molecular)
-
Dot-and-cross diagrams for:
Draw your diagrams in the spaces below:
a) Hydrogen fluoride, HF:
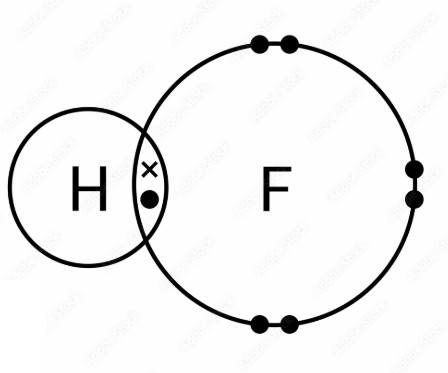
b) Fluorine, F2:
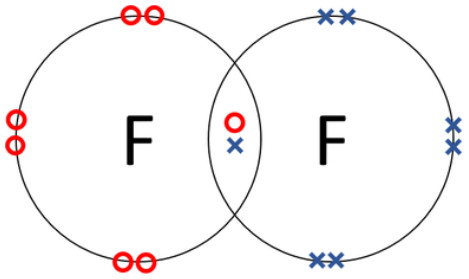
c) Silicon tetrachloride, SiCl4:
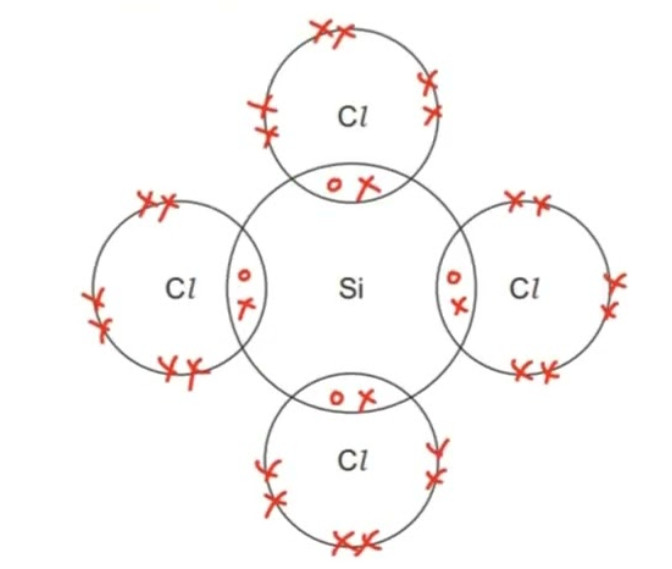
d) Hydrogen sulfide, H2S:
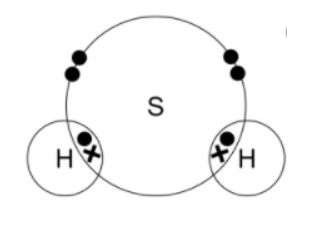
-
Complete the dot-and-cross diagrams:
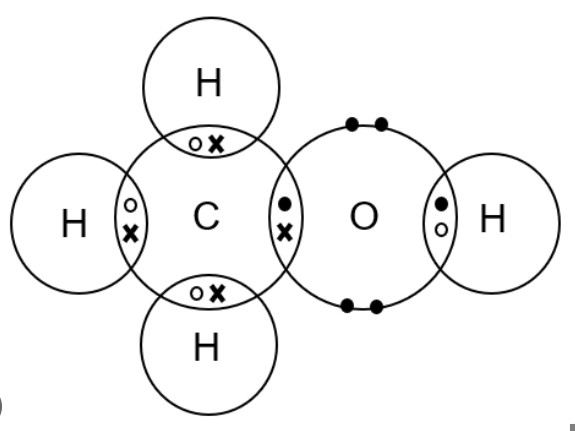
a) Ethanol, C2H5OH:
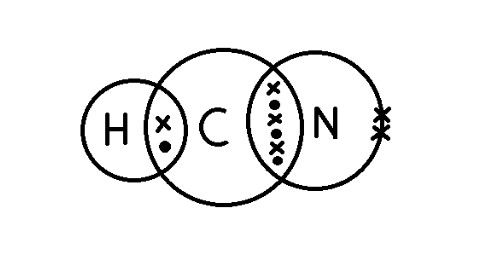
b) Hydrogen cyanide, HCN:
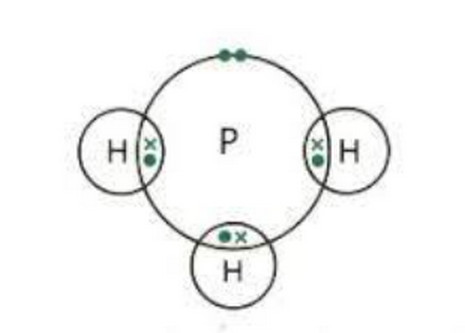
c) Phosphine, PH3:
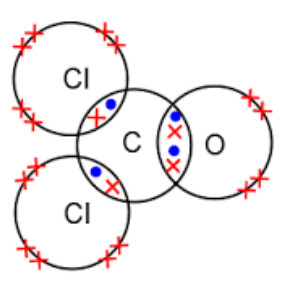
d) Carbonyl chloride, COCl2:
-
Ionic compound formulae:
- a) Calcium hydroxide = Ca(OH)2
- b) Magnesium chloride = MgCl2
- c) Ammonium phosphate = (NH4)3PO4
- d) Lithium sulfide = Li2S
- e) Lead(II) nitrate = Pb(NO3)2
- f) Calcium carbonate = CaCO3
- g) Aluminium nitrate = Al(NO3)3
- h) Potassium sulfite = K2SO3
- i) Zinc sulfate = ZnSO4
- j) Ammonium sulfate = (NH4)2SO4
-
Balanced equations:
a) CaC2 + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + C2H2
b) 2KOH + H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2H2O
c) TiCl4 + 4Na → Ti + 4NaCl
d) 2KO2 + 2CO2 → 2K2CO3 + O2
e) 2Al + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2
-
Concentration calculations:
a) For NaOH:
- Volume in dm³ = 500/1000 = 0.5 dm³
- Concentration = 20.0/0.5 = 40.0 g/dm³
b) For K2SO4:
- Volume already in dm³ = 2 dm³
- Concentration = 17.4/2 = 8.7 g/dm³
-
For carbon atoms:
- Number of moles = mass/Ar
- = 6.0/12
- = 0.5 moles
-
For H2 molecules:
- Mr of H2 = 2
- Number of moles = 3.0/2 = 1.5 moles
- Number of molecules = 1.5 × 6.022 × 1023
- = 9.033 × 1023 molecules
Answers – Homework – 1
Powered by BetterDocs




