Geography Exam Answers – Rivers and Drainage Basins #
Question 1(a): Storm Hydrographs #
(i) River discharge is the amount of water flowing in a river.
Tick the one formula in the table below which shows how river discharge is calculated.
[1]width × depth × speed of flow
precipitation × volume of river
speed of flow × amount of erosion
groundwater flow × overland flow
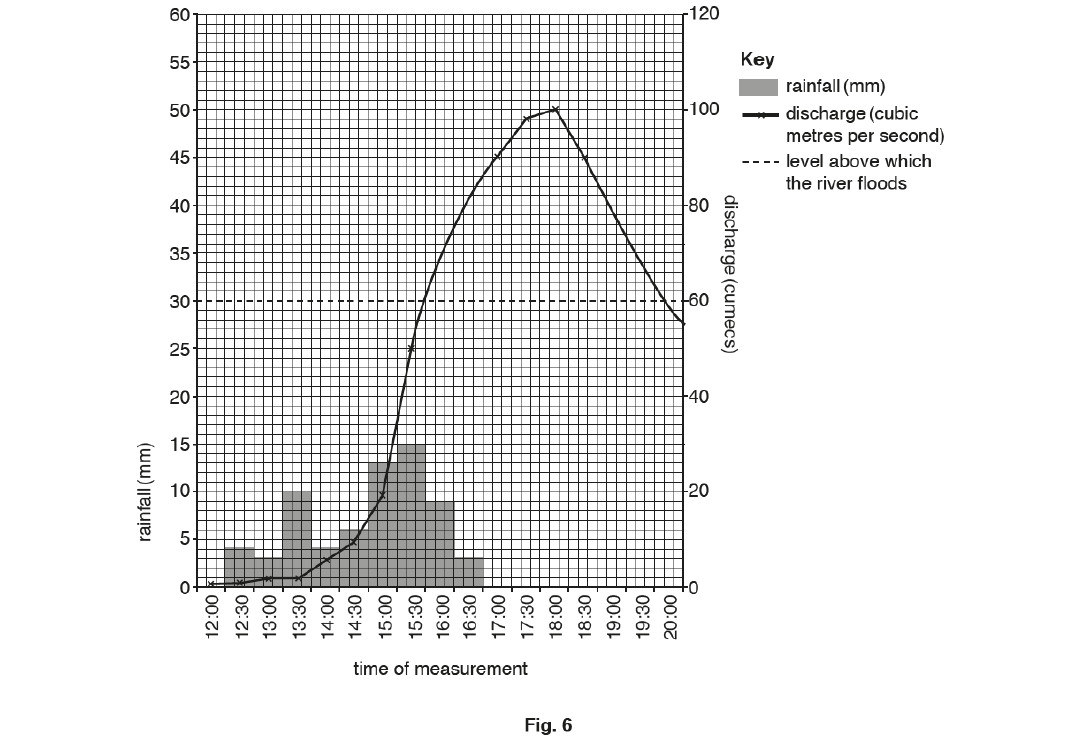
(ii) Identify from Figure 6:
• the maximum rainfall during 30 minutes
• the time when the river was most likely to start flooding
[2]- Maximum rainfall during 30 minutes: 15 mm
- Time when river most likely to start flooding: 17:30
(iii) Explain why rivers sometimes continue to flood for many hours after the end of a period of heavy rain.
[3]Water takes time to flow from far places to the river. Some water goes underground first and moves slowly. The ground is already full of water so new rain runs straight to the river. All this water keeps coming even after rain stops.
(iv) Explain why an increase in discharge of a river will influence the amount of erosion and transportation taking place.
[4]More water makes the river flow faster. Fast water has more power to pick up rocks and mud from the bottom. It can carry bigger pieces of rock. The strong water also breaks away the river banks.
Question 1(b): Drainage Basins and Deforestation #
(i) What is meant by the following terms:
• drainage basin
• watershed
• tributary
[3]- Drainage basin: The area of land drained by a river and all its tributaries
- Watershed: The high land that separates one drainage basin from another
- Tributary: A smaller river that flows into a larger river
(ii) Describe the problems for people and the natural environment in Oregon which may be caused by increased deforestation.
[5]Problems for people:
- Increased flooding as trees no longer intercept rainfall
- Water pollution from soil erosion getting into rivers
- Loss of jobs in forestry and tourism
- Damage to property from landslides on steep slopes
Problems for natural environment:
- Loss of animal habitats and food sources
- Soil erosion as tree roots no longer hold soil together
- Climate change as fewer trees to absorb carbon dioxide
- Loss of biodiversity as species lose their homes
Question 1(c): Opportunities of Living Near Rivers #
Describe the opportunities of living near a named river you have studied.
[5]Name of river: River Thames
Opportunities:
- Water supply: Fresh water for drinking, washing and industry
- Transport: Ships and boats can carry goods and people cheaply
- Agriculture: Fertile soil in the flood plain for growing crops
- Fishing: Source of food and income from catching fish
- Tourism: River cruises and water sports bring visitors and money
- Industry: Water for cooling in power stations and factories
- Trade: Ports and harbors for importing and exporting goods
- Hydroelectric power: Using flowing water to generate electricity
- Recreation: Swimming, boating and fishing for leisure
- Settlement: Flat land for building houses and cities




