Absolutely! Here’s a simpler explanation of each section for your biology notes:
Biological molecules are important substances that make up all living things and help them function. There are different types of biological molecules, including carbohydrates, proteins, lipids (which include fats and oils), and DNA. Each type has specific roles in our bodies and other living organisms.
1. Carbohydrates #
Introduction:
Carbohydrates are a type of molecule that provides energy for our bodies. They are found in many of the foods we eat, like bread, rice, and fruits.
What They’re Made Of:
Carbohydrates are made from three elements: carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
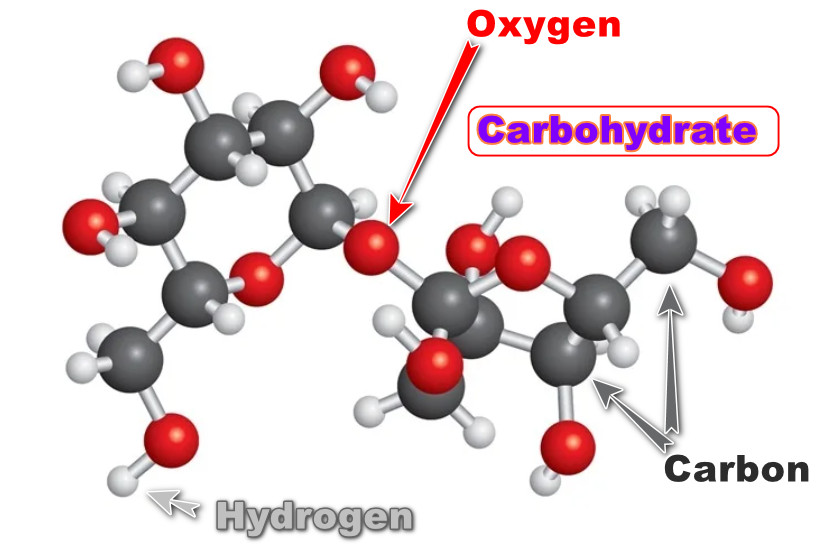
Example of carbohydrate:
- Simple Sugars: Like glucose (a type of sugar) which our bodies use for quick energy.
- Complex Carbohydrates: These are long chains of sugar units. They include:
- Starch: Found in foods like potatoes and rice; it stores energy for plants.
- Cellulose: Helps form the cell walls in plants; it’s what makes up fiber in vegetables.
- Glycogen: How animals store energy, especially in muscles and the liver.
Functions of carbohydrates
- Energy Source: Carbohydrates give us energy, especially when we need a quick boost.
- Energy Storage: Plants store energy as starch, while animals store it as glycogen.
- Cell Structure: Carbohydrates like cellulose help give plants their structure and strength.
2. Proteins #
Introduction:
Proteins are essential molecules made up of amino acids. They help build and repair tissues, and they are involved in many functions in our bodies.
Detailed Explanation:
- What They’re Made Of: Proteins are made from smaller units called amino acids. These amino acids are connected together in a chain.
- Structure: Proteins can be thought of like a necklace with many beads (amino acids). The order of the beads determines what the protein does.
Amino Acid
Each amino acid has a central carbon atom, an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a unique side chain.
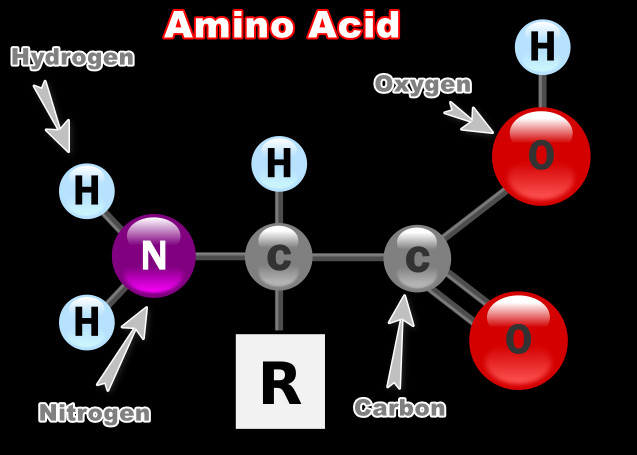
Function of proteins
- Building Blocks: Proteins are used to build and repair muscles, skin, and other tissues.
- Examples:
- Keratin: Found in hair and nails.
- Collagen: Found in skin and connective tissues.
- Enzymes: Proteins that help speed up chemical reactions in the body.
3. DNA #
Introduction:
DNA is like a instruction manual for living things. It carries all the information needed to make and maintain an organism.
Detailed Explanation:
- What it Stands For: DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid.
- Composition: DNA is made up of three parts:
- Phosphate Group: A small molecule that helps form the backbone of DNA.
- Sugar: Called deoxyribose, it connects with the phosphate group.
- Nitrogen Bases: Four types of bases (Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine) that pair up to form the steps of the DNA ladder. Diagram of DNA Structure:

- Functions:
- Genetic Information: DNA carries the instructions for how to build and operate every part of a living thing.
- Protein Making: DNA helps cells make proteins by providing the instructions needed.
- Inheritance: DNA is passed from parents to their children, which is why you might have similar traits to your family members.
4. Fats and Oils #
Introduction:
Fats and oils are types of molecules that store energy and help protect and insulate our bodies. They are important for overall health.
Detailed Explanation:
- What They’re Made Of: Fats and oils are made from carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They have a structure where one part (glycerol) is connected to three long chains (fatty acids).
- Structure: Think of fats like a small tree with a trunk (glycerol) and three branches (fatty acids) sticking out. Diagram of Fats/Oils Structure:

- Functions:
- Energy Storage: Fats provide a lot of energy and are stored in the body for later use.
- Insulation: Fats help keep your body warm by providing insulation.
- Protection: Fats protect vital organs by cushioning them.
QUESTIONS
- What are carbohydrates?
- What three elements make up carbohydrates?
- What is an example of a simple sugar?
- What are complex carbohydrates?
- How do plants store energy?
- What role does cellulose play in plants?
- What is glycogen and where is it stored?
- What are proteins made of?
- What is the structure of a protein compared to?
- Name one protein found in hair and nails.
- What is collagen and where is it found?
- What is the full form of DNA?
- What are the three parts of a DNA molecule?
- Name the four types of nitrogen bases in DNA.
- What role does DNA play in inheritance?
ANSWERS
- Carbohydrates are molecules that provide energy for our bodies. They are found in foods like bread, rice, and fruits.
- Carbohydrates are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
- Glucose is an example of a simple sugar that our bodies use for quick energy.
- Complex carbohydrates are long chains of sugar units. Examples include starch, cellulose, and glycogen.
- Plants store energy as starch.
- Cellulose helps form the cell walls in plants and makes up fiber in vegetables.
- Glycogen is how animals store energy, and it is stored in muscles and the liver.
- Proteins are made of amino acids connected in chains.
- Proteins can be thought of like a necklace with many beads (amino acids), where the order of the beads determines the protein’s function.
- Keratin is a protein found in hair and nails.
- Collagen is a protein found in skin and connective tissues.
- DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid.
- The three parts of a DNA molecule are the phosphate group, sugar (deoxyribose), and nitrogen bases.
- The four types of nitrogen bases in DNA are Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, and Guanine.
- DNA is passed from parents to their children, which is why you might have similar traits to your family members.




