Table of Contents
What are Covalent Bonds? #
Covalent bonds form when two or more non-metal atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, typically resembling the noble gases.
- Each atom contributes an equal number of electrons to the shared pair(s).
- These bonds hold the atoms together in molecules.
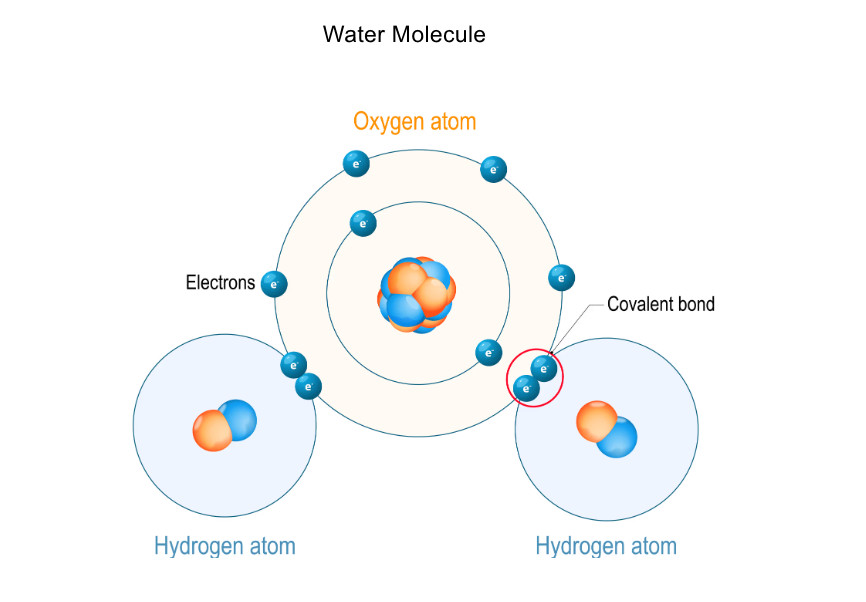
Why Do Covalent Bonds Form? #
Atoms form covalent bonds to become more stable by:
- Atoms aim for a complete valence shell (the outer orbit or electrons), often eight electrons
- Sharing electrons stabilizes the molecule.
- Sharing electrons is more energy-efficient for non-metals than losing or gaining them.
Characteristics of Covalent Bonds #
- Formed Between: Non-metal atoms.
- Bond Strength: Generally strong due to the sharing of electrons.
Examples of Covalent Bonds in Daily Life #
- Water (H₂O): Oxygen shares electrons with two hydrogen atoms.
- Oxygen Gas (O₂): Two oxygen atoms share two pairs of electrons, forming a double bond.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): Carbon shares electrons with two oxygen atoms, forming two double bonds.




