Types of Deltas #
IGCSE Geography Topic 1.2 – Understanding the different shapes and forms of deltas
The Three Main Types of Deltas #
Deltas are grouped into three main types based on their shape: arcuate (fan-shaped), bird’s foot (digitate), and cuspate (pointed).
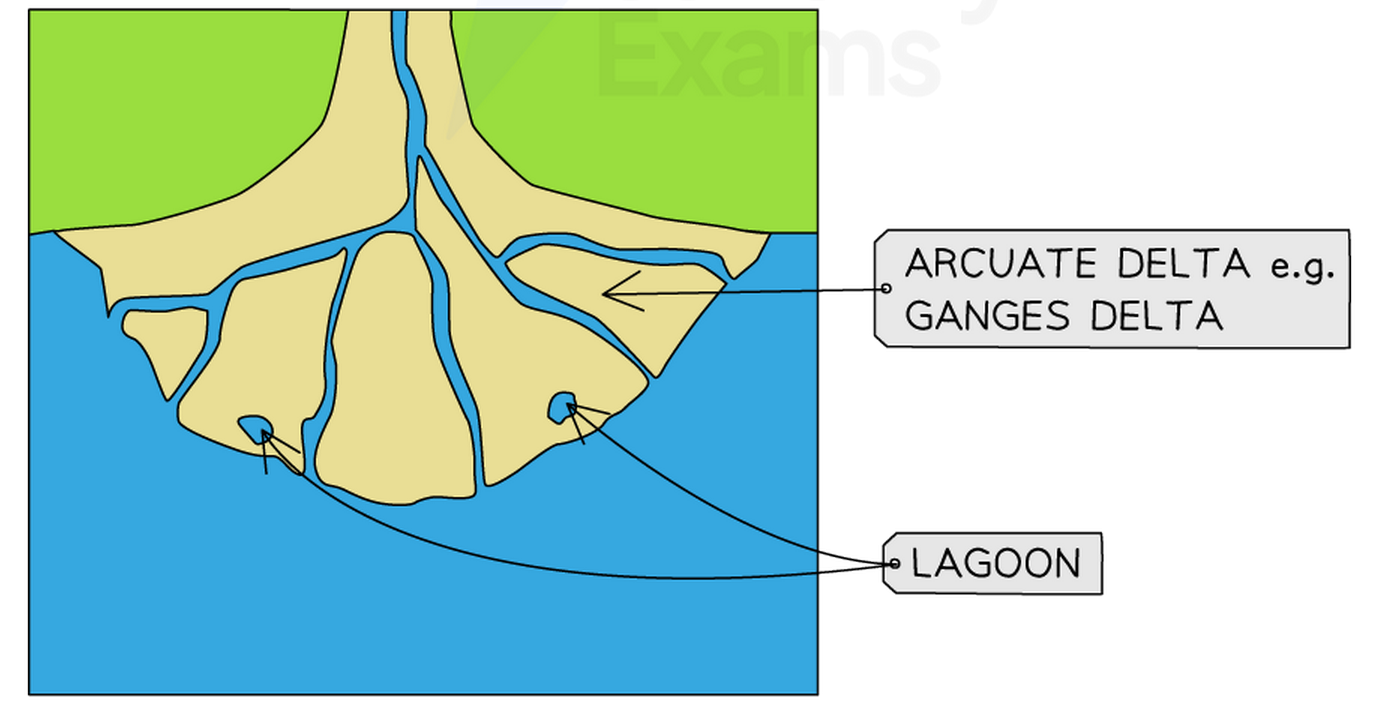
1. Arcuate (Fan-Shaped) Deltas #
Arcuate deltas are the most common type. They have a wide, curved triangular shape like an open fan. The word “arcuate” means curved or arc-shaped.
These deltas form when the river brings lots of sediment, but waves are strong enough to spread it evenly along the coast. The waves smooth out the delta’s edge, creating the curved, fan-like shape.
- Wide, fan-shaped triangular appearance
- Smooth, curved outer edge
- Multiple distributary channels spreading across the delta
- Relatively smooth and regular shoreline
2. Bird’s Foot (Digitate) Deltas #
Bird’s foot deltas have a distinctive shape that looks like a bird’s foot with long, thin “toes” stretching into the sea. The geographical term is “digitate delta” (digitate means finger-like), but they’re commonly called bird’s foot deltas.
These form when a powerful river carrying huge amounts of sediment meets a very calm sea with weak waves and tides. With no strong waves to spread sediment sideways, the river dumps material straight ahead, creating long finger-like projections extending into the sea.
- Long, narrow projections extending into the sea like fingers
- Each “finger” is an active river channel
- Very irregular coastline with deep bays between fingers
- Channels extend far from the original coastline

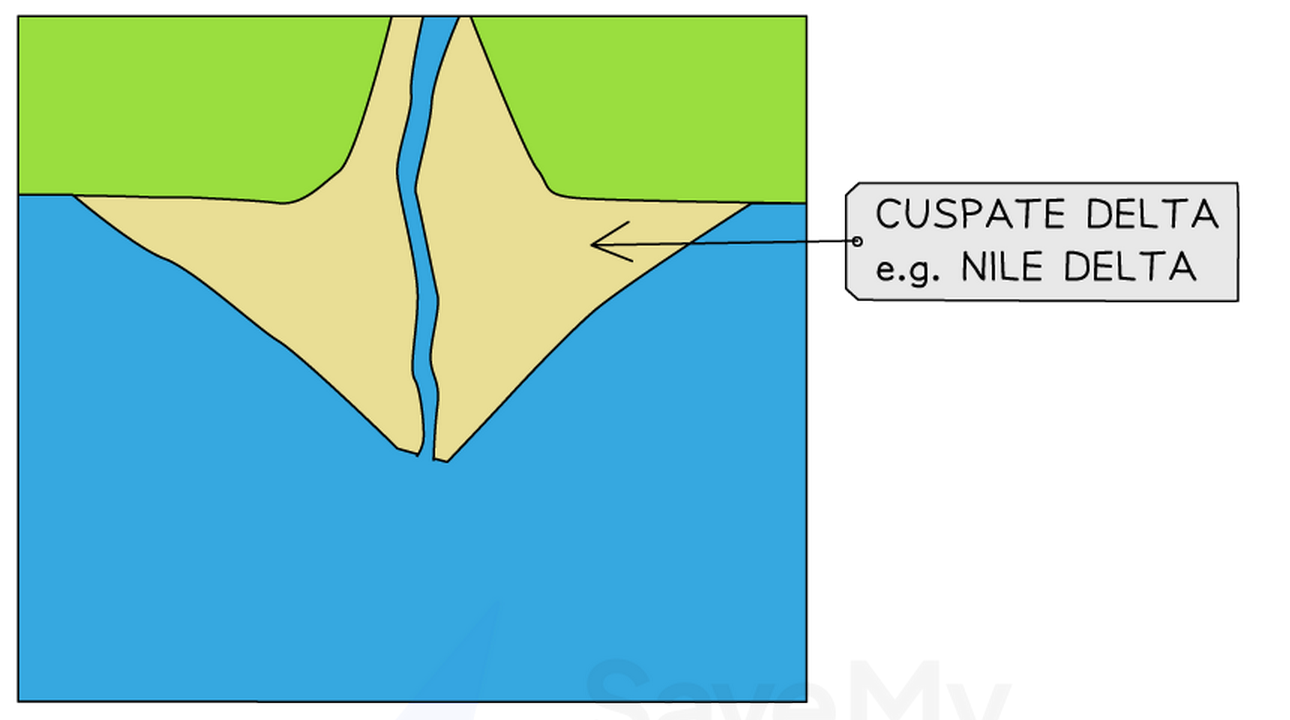
3. Cuspate Deltas #
Cuspate deltas are the rarest type. “Cuspate” means pointed or tooth-shaped. These deltas have a distinctive triangular, pointed shape like an arrowhead pointing into the sea.
Cuspate deltas form where waves approach the river mouth from two different directions (usually from both sides). These opposing waves push sediment toward the center, creating a pointed shape.
- Sharp, pointed triangular shape like an arrowhead
- Single prominent point extending into the sea
- Relatively symmetrical on both sides
- Much smaller than arcuate or bird’s foot deltas
Comparing Delta Types #
| Feature | Arcuate | Bird’s Foot | Cuspate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shape | Fan-shaped triangle | Long fingers like bird’s toes | Pointed arrowhead |
| River Power | Strong | Very strong | Moderate |
| Wave Strength | Moderate | Very weak | Strong (two directions) |
| Coastline | Smooth, curved | Very irregular | Central point |
| Example | Nile Delta | Mississippi Delta | Ebro Delta |
| Frequency | Most common | Uncommon | Rare |




