Topic 3.1 Revision Test
Time: 90 minutes | Total: 50 questions
SECTION A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS #
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question. Write the letter (A, B, C, or D) in your answer booklet.
1. What do waves transfer from one place to another?
2. A student creates waves in a rope by moving one end up and down. What stays in the same place as the wave travels along the rope?
3. The distance between two identical points on a wave is called the:
4. The amplitude of a wave measures:
5. If a wave has a frequency of 10 Hz, this means:
6. Using the wave equation $v = f\lambda$, if frequency increases and wave speed stays constant, what happens to wavelength?
7. Water waves have a wavelength of 2 m and travel at 6 m/s. What is their frequency?
8. In a transverse wave, particles of the medium vibrate:
9. Which of these is an example of a transverse wave?
10. In longitudinal waves, particles vibrate:
11. Sound waves traveling through air are:
12. Which of these waves can travel through empty space?
13. When a wave is reflected from a surface, the angle of incidence:
14. Refraction occurs when waves:
15. When light waves slow down as they enter glass from air, they bend:
16. Diffraction is most noticeable when the wavelength is:
17. You can hear someone talking around a corner because sound waves undergo:
18. In a ripple tank, we use shallow water to demonstrate:
19. Seismic P-waves are:
20. Which wave property determines how much energy a wave carries?
21. A wave has crests and troughs. This wave is:
22. In a longitudinal wave, the areas where particles are pushed together are called:
23. A wavefront is:
24. When using a ripple tank, what makes the wave patterns visible?
25. If the frequency of water waves increases while their speed stays constant, what happens to their wavelength?
26. Which statement about electromagnetic waves is correct?
27. Water waves in a ripple tank travel from deep water into shallow water. What happens to their speed?
28. A wave is diffracted as it passes through a gap. For maximum diffraction to occur, the gap width should be:
29. Seismic S-waves cannot travel through the Earth’s liquid outer core because:
30. Which wave behavior explains why you can see your reflection in a mirror?
SECTION B: STRUCTURED QUESTIONS #
Instructions: Answer all questions. Show your working for calculations. Use appropriate units in your answers.
31. The diagram shows a wave.
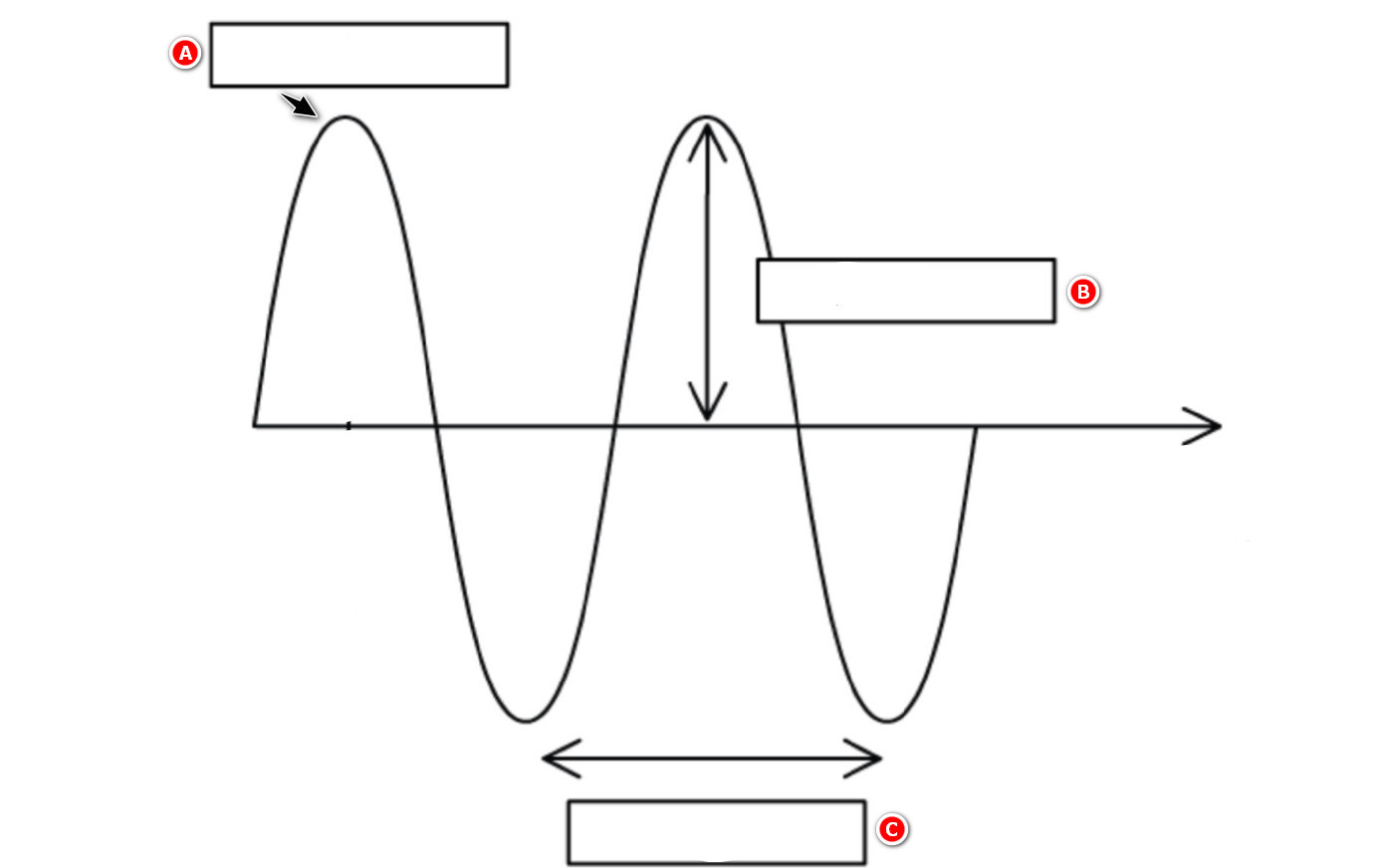
a) Draw this diagram and label the following on the diagram: [3 marks]
(i) One complete wavelength
(ii) The amplitude
(iii) A crest
b) Explain what is meant by the amplitude of a wave. [2 marks]
32. A student investigates water waves using a ripple tank.
a) Describe how waves transfer energy without transferring matter. [3 marks]
b) The student creates water waves with a frequency of 4 Hz and wavelength of 0.5 m. Calculate the speed of these waves. [3 marks]
Formula: $v = f\lambda$
33. Complete the table to show the differences between transverse and longitudinal waves. [6 marks]
| Property | Transverse waves | Longitudinal waves |
|---|---|---|
| Direction of particle vibration compared to wave direction | _______________________ | _______________________ |
| Example of this type of wave | _______________________ | _______________________ |
| Special features of the wave | Has crests and __________ | Has compressions and __________ |
34. Sound waves travel at 340 m/s in air. A sound wave has a frequency of 680 Hz.
a) Calculate the wavelength of this sound wave. [3 marks]
Formula: $v = f\lambda$, so $\lambda = \frac{v}{f}$
b) Explain why this sound wave is a longitudinal wave. [2 marks]
35. The diagram shows wave reflection at a plane surface.
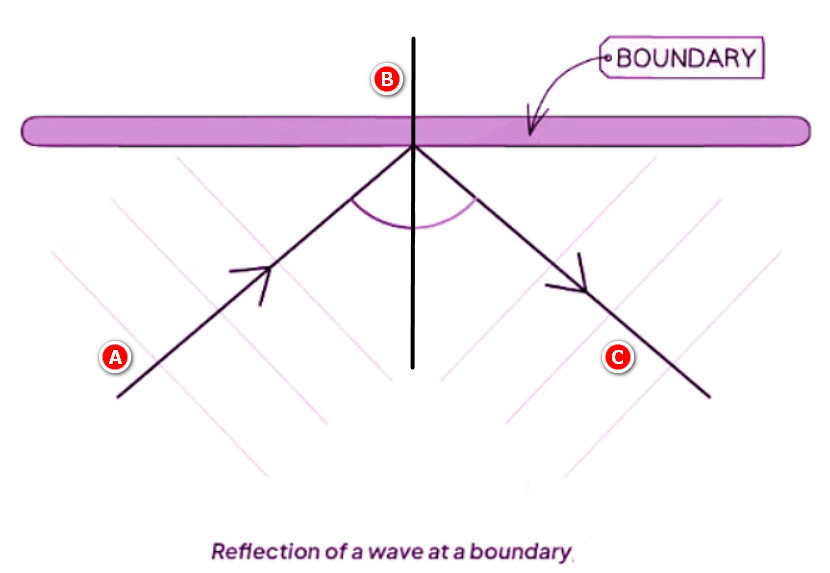
a) On the diagram, label: [3 marks]
(i) The incident wave
(ii) The reflected wave
(iii) The normal
b) State the law of reflection. [2 marks]
36. A student uses a ripple tank to study refraction.
a) Explain what happens to water waves when they travel from deep water to shallow water. [3 marks]
b) Explain why refraction causes waves to change direction. [2 marks]
37. The diagram shows diffraction of water waves passing through a gap.
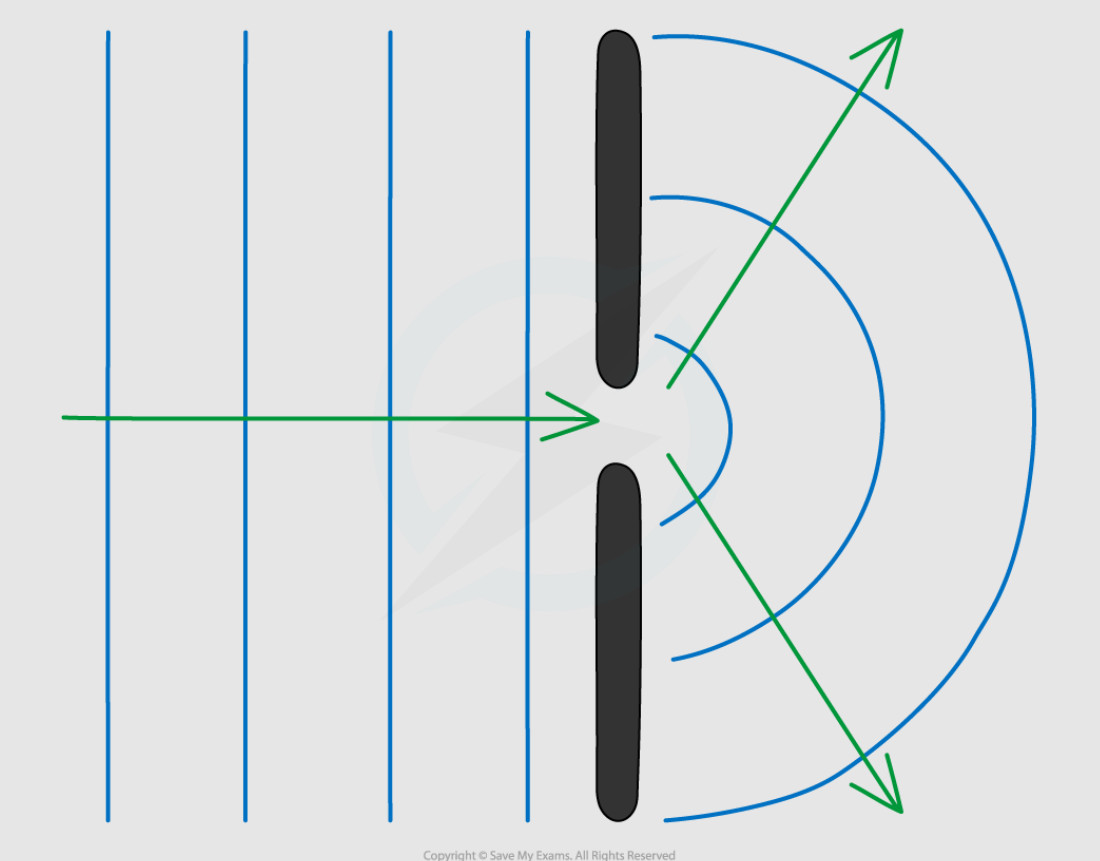
a) Describe what happens to the wave pattern after the waves pass through the gap. [2 marks]
b) State one factor that affects how much diffraction occurs. [1 mark]
c) Give one example of diffraction that you might observe in everyday life. [1 mark]
38. Radio waves have a frequency of 100 MHz (100,000,000 Hz) and travel at 300,000,000 m/s.
a) Calculate the wavelength of these radio waves. [3 marks]
b) Explain why radio waves can reach areas that seem to be blocked by buildings. [2 marks]
39. A vibrating guitar string produces sound waves with a frequency of 440 Hz. The speed of sound in air is 340 m/s.
a) Calculate the wavelength of the sound waves in air. [3 marks]
b) The same string is now pressed to make it shorter. Explain what happens to: [4 marks]
(i) The frequency of the sound
(ii) The wavelength of the sound
40. Describe how you could use a ripple tank to demonstrate reflection of water waves. Include: [6 marks]
a) What equipment you would need
b) How you would set up the experiment
c) What you would observe
41. Light waves and sound waves behave differently when they encounter obstacles.
a) Explain why you can hear someone talking around a corner but you cannot see them until they come into view. [4 marks]
b) State which wave property determines how much diffraction occurs. [1 mark]
42. Water waves travel at different speeds in deep and shallow water.
a) A wave has a speed of 2.0 m/s and frequency of 0.5 Hz in deep water. Calculate its wavelength. [3 marks]
b) The same wave slows to 1.0 m/s when it enters shallow water. The frequency stays the same. Calculate the new wavelength. [3 marks]
c) Explain why the frequency stays the same when the wave enters shallow water. [2 marks]
43. Seismic waves are produced during earthquakes.
a) Name the two main types of seismic waves. [2 marks]
b) Explain the difference between these two types of waves. [4 marks]
c) Explain why only one type of seismic wave can travel through the Earth’s liquid outer core. [2 marks]
44. A student observes that when light passes from air into a glass block, it bends toward the normal.
a) Name this wave behavior. [1 mark]
b) Explain why this bending occurs. [3 marks]
c) Predict what would happen to the light when it exits the glass block back into air. [2 marks]
45. Electromagnetic waves include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
a) State two properties that are the same for all electromagnetic waves. [2 marks]
b) State two properties that are different for different types of electromagnetic waves. [2 marks]
46. The diagram shows displacement against time for a wave.
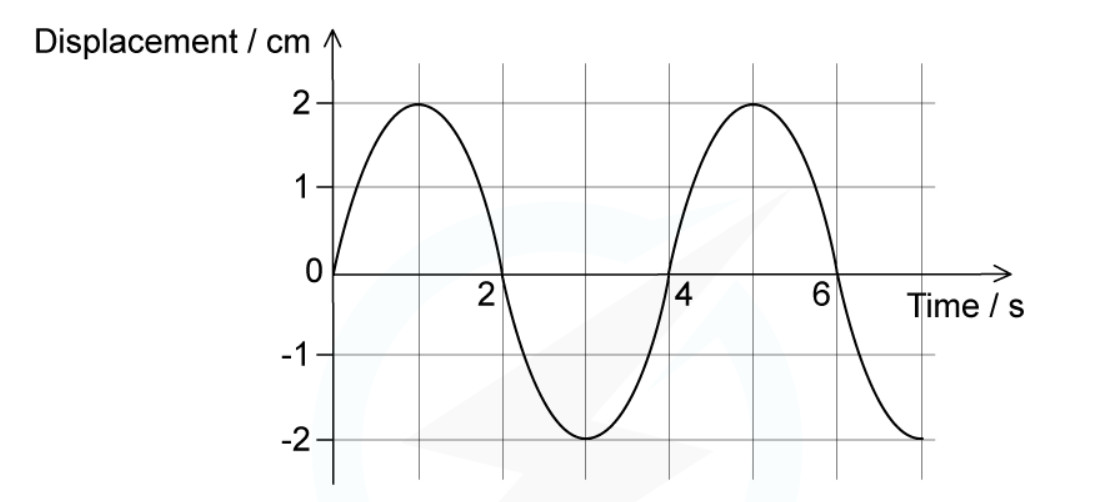

a) Use the graph to find the frequency of this wave. [2 marks]
b) If this wave travels at 1.0 m/s, calculate its wavelength. [3 marks]
47. A student places a barrier with a small gap in a ripple tank and observes the water waves.
a) Describe what happens to the waves after they pass through the gap. [2 marks]
b) The student then makes the gap much larger. Predict how this will affect the wave pattern and explain your answer. [3 marks]
48. Ocean waves approach a straight coastline. The diagram shows the wave pattern.
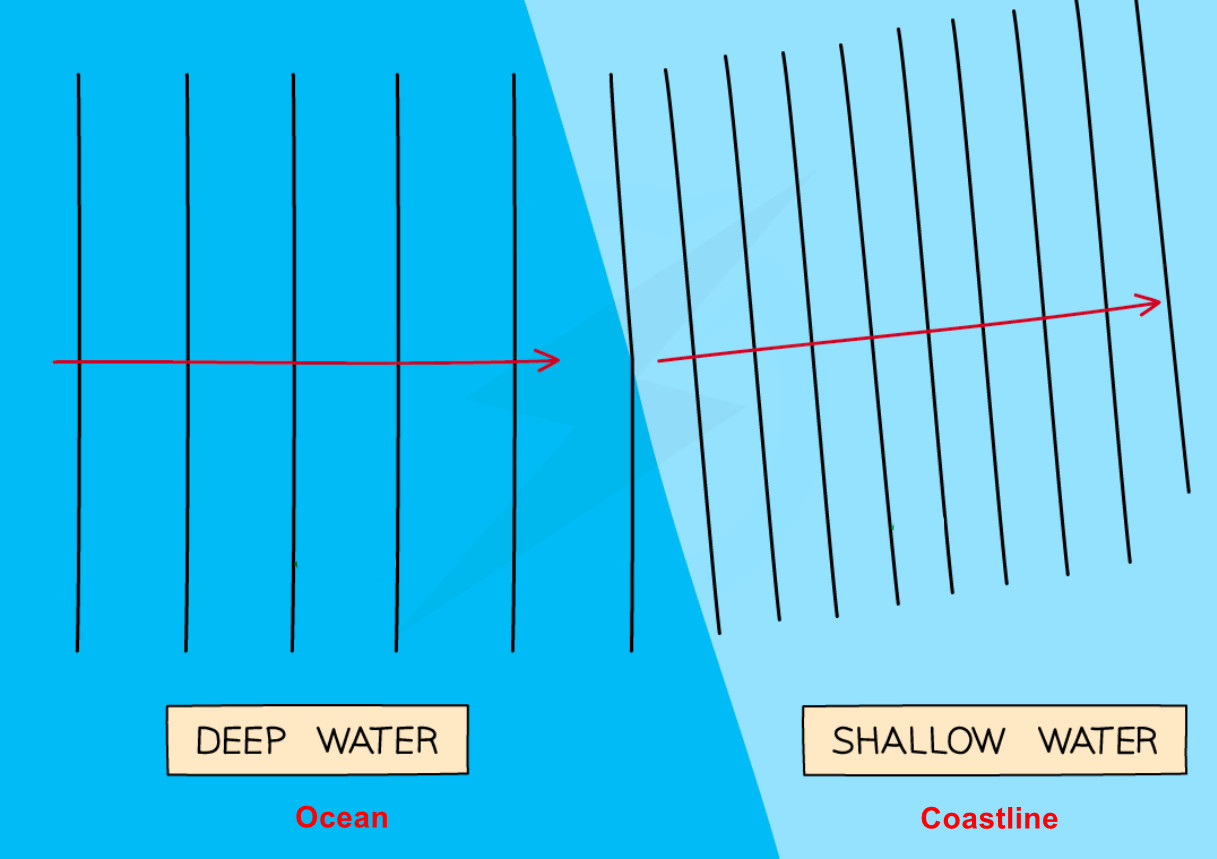

a) Explain why the wave fronts change direction as they approach the shore. [3 marks]
b) Name the wave behavior shown in this diagram. [1 mark]
49. A physics teacher demonstrates wave motion using a long spring.
a) Describe how the teacher could create transverse waves in the spring. [2 marks]
b) Describe how the teacher could create longitudinal waves in the same spring. [2 marks]
c) Explain what both types of waves transfer along the spring. [1 mark]
50. Two students investigate wave speed using a ripple tank. They measure the following data:
| Trial | Frequency (Hz) | Wavelength (cm) | Wave speed (cm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.0 | 5.0 | _______ |
| 2 | 3.0 | _______ | 12.0 |
| 3 | _______ | 3.0 | 15.0 |
a) Complete the table by calculating the missing values. Show your working for each calculation. [6 marks]
Formula: $v = f\lambda$
b) The students notice that when they increase the frequency, the wavelength changes. Explain why this happens if the wave speed stays constant. [2 marks]
END OF TEST
Revision Tips: #
- Wave Equation: Always remember $v = f\lambda$ – practice rearranging this formula
- Wave Types: Transverse (perpendicular vibration) vs Longitudinal (parallel vibration)
- Wave Behaviors: Reflection (bouncing), Refraction (bending due to speed change), Diffraction (spreading through gaps)
- Key Concept: Waves transfer energy, not matter – particles vibrate in place while energy travels
- Practical Skills: Know how to use a ripple tank to demonstrate all wave properties




