-
a) Complete the table below, showing the charge on each particle.
Particle Number of protons Number of electrons Number of neutrons Charge on particle A 20 18 18 B 17 17 20 C 9 9 10 D 17 17 18 E 13 10 14 F 16 18 19 b) State the nucleon number of E.
c) Give the letters of the two particles that are isotopes.
d) State the name of the element that contains particles of F.
-
Complete the table below.
Particle Number of protons Number of electrons Electronic configuration Charge on particle A 20 18 B 9 10 2,8 C 10 2,8 0 D 8 10 2,8 -
The diagram below shows the structures of five different substances.
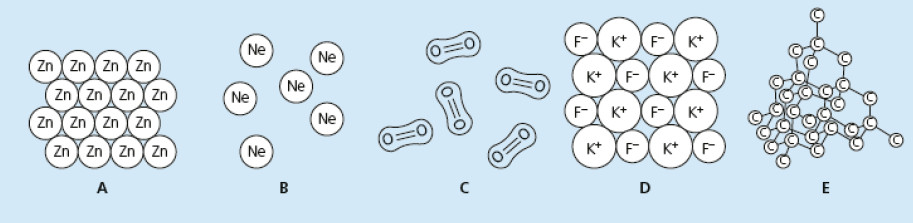
Use the letters A, B, C, D and E to answer the questions below.
Each letter may be used once, more than once or not at all.Give the letter that shows:
a) atoms with a full outer shell of electrons
b) a giant covalent structure
c) particles that are formed by loss and gain of electrons
d) a substance that conducts electricity when solid
e) a substance that only conducts electricity when molten or dissolved in water
f) the substance with the lowest melting point
-
Draw the dot-and-cross diagrams to show the electronic configurations (outer shells only) of the following molecules.
a) hydrogen fluoride, HF
b) fluorine, F₂
c) silicon tetrachloride, SiCl₄ (the atoms are arranged in the same way as in methane, CH₄)
d) hydrogen sulfide, H₂S (the atoms are arranged in the same way as in water, H₂O)
-
Complete the dot-and-cross diagrams below to show the electronic configurations (outer shells only) of the following molecules. [Total: 4]
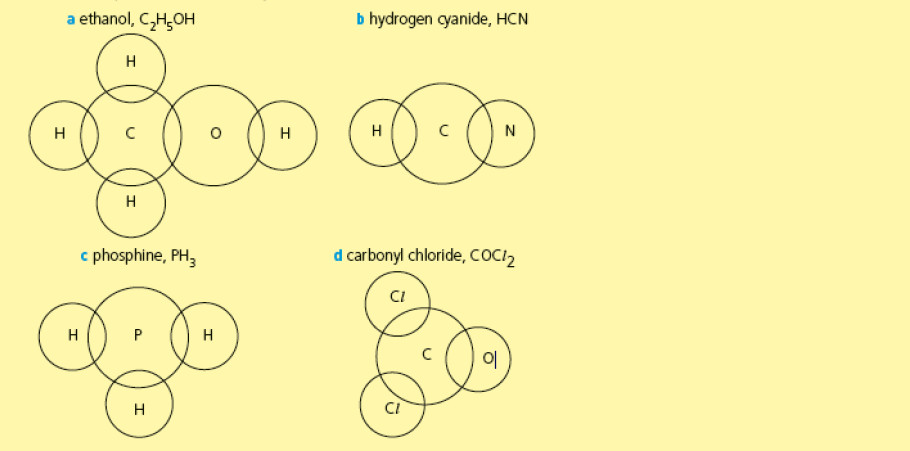
-
Deduce the formulae of the following ionic compounds
a) calcium hydroxide
b) magnesium chloride
c) ammonium phosphate
d) lithium sulfide
e) lead(II) nitrate
f) calcium carbonate
g) aluminium nitrate
h) potassium sulfite
i) zinc sulfate
j) ammonium sulfate
-
Balance the following chemical equations. Some of the balancing numbers have been added for you.
a) CaC₂(s) + ___ H₂O(l) → Ca(OH)₂(aq) + C₂H₂(g)
b) ___ KOH(aq) + H₂SO₄(aq) → K₂SO₄(aq) + ___ H₂O(l)
c) TiCl₄(l) + ___ Na(s) → Ti(s) + ___ NaCl(s)
d) ___ KO₂(s) + ___CO₂(g) → 2K₂CO₃(g) + ___ O₂(g)
e) ___ Al(s) + 6HCl(aq) → ___ AlCl₃ + ___ H₂(g)
-
Calculate the concentration in g/dm³ of a solution containing:
a) 20.0 g of NaOH in 500 cm³
b) 17.4 g of K₂SO₄ in 2 dm³
-
Calculate the Mr of the following compounds:
a) glucose, C₆H₁₂O₆
b) hydrated sodium sulfate, Na₂SO₄.10H₂O
c) potassium dichromate(VI), K₂Cr₂O₇
-
6.0 g of magnesium ribbon burns in excess oxygen to form 10.0 g of magnesium oxide.
a) State what is meant by excess oxygen in the statement above.
b) State the mass of magnesium oxide that would form if 18.0 g of magnesium ribbon was burnt in excess oxygen.
c) State the mass of magnesium ribbon that would be burned in excess oxygen to form 0.24 g of magnesium oxide.
-
Calculate the number of moles in 6.0 g of carbon atoms. Ar of C = 12.
-
Calculate the number of molecules in 3.0 g of hydrogen molecules, H₂.
Test – Homework – 1
Powered by BetterDocs




