Understanding Mass, Weight, and Density in Physics #
To understand how objects behave in the physical world, we need to understand three important concepts: mass, weight, and density. These properties help us explain everything from why some objects float to why things feel heavier on Earth than they would on the Moon.
1. Understanding Mass #
Mass is the amount of matter in an object. Unlike weight, mass stays the same no matter where you are in the universe.
Key Points About Mass: #
- Unit: Measured in kilograms (kg) or grams (g)
- Constant: Doesn’t change with location
- Measurement: Using a balance (comparing with known masses)
2. Understanding Weight #
Weight is the force of gravity acting on an object’s mass. Unlike mass, weight changes depending on the gravitational field strength.
The Weight Formula #
Weight = Mass × Gravitational Field Strength
W = m × g
Where:
- W = weight in Newtons (N)
- m = mass in kilograms (kg)
- g = gravitational field strength in N/kg
Weight on Different Planets #
| Location | Gravitational Field Strength (N/kg) |
|---|---|
| Earth | 9.81 |
| Moon | 1.62 |
| Mars | 3.72 |
3. Understanding Density #
Density is how much mass is packed into a given volume. It helps us understand why some objects float while others sink.
The Density Formula #
Density = Mass ÷ Volume
ρ = m ÷ V
Where:
- ρ (rho) = density in kg/m³ or g/cm³
- m = mass in kg or g
- V = volume in m³ or cm³
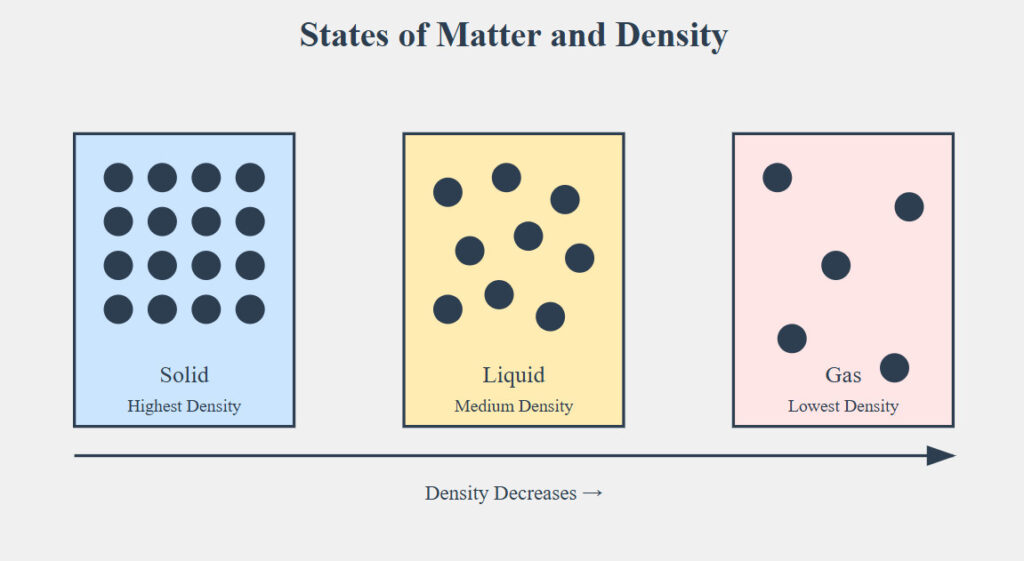
4. States of Matter and Density #
5. Real-World Applications #
Examples in Daily Life: #
- Mass vs Weight: Astronauts have the same mass but different weights in space
- Density in Nature: Ice floating because it’s less dense than liquid water
- Engineering: Choosing materials based on their density for different applications
- Transportation: Hot air balloons work because hot air is less dense than cool air
Solids are more dense that gases #
Solids have more mass than gasses and so in the same volume, the solids will have a higher density